=================================================================================
The resolution for light microscope is defined by Rayleigh criterion,
δ = 0.61λ/μ sinβ ------------------------- [4526]
where λ -- Wavelength of the light
μ -- Refractive index of the viewing medium
β -- Semiangle of collection of the magnifying lens
For your memory, you can approximate “μ sinβ” to unity, so that the resolution is equal to about half the wavelength of light. For instance, for green light in the middle of the visible spectrum, λ is about 550 nm, so the resolution of a good light microscope is about 275 nm (300 nm more accurately).
Figure 4526 shows the typical sizes of various material defects and the capability of analytical techniques (See the full names of the techniques at page3928). The lowest levels of the techniques represent their spatial resolutions.
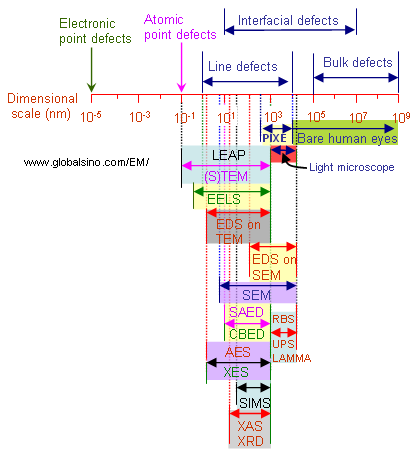
Figure 4526. Typical sizes of various material defects and capability of analytical techniques.
|