NaN stands for Not a Number. Handling NaN (Not a Number) values in a DataFrame is an essential task in data analysis and preprocessing. Pandas, a popular Python library for data manipulation, provides several methods to handle NaN values in DataFrames effectively:
-
Detect NaN Values: Before handling NaN values, it's crucial to identify where they exist in your DataFrame. You can use the isna() or isnull() method to detect NaN values.
import pandas as pd
# Detect NaN values
nan_df = df.isna()
- Remove NaN Values: You can remove rows or columns containing NaN values using the dropna() method.
# Remove rows with NaN values
cleaned_df = df.dropna()
# Remove columns with NaN values
cleaned_df = df.dropna(axis=1)
- Fill NaN Values: Instead of removing NaN values, you can fill them with a specified value using the fillna() method.
# Fill NaN values with a specific value, e.g., 0
filled_df = df.fillna(0)
# Fill NaN values with the mean of the column
filled_df = df.fillna(df.mean())
- Interpolation: For time-series data, you might want to interpolate NaN values based on neighboring values.
# Interpolate NaN values linearly
interpolated_df = df.interpolate(method='linear')
- Customized Handling: You can also define custom strategies to handle NaN values based on your data and requirements.
# Replace NaN values with a custom value based on conditions
df['column_name'].fillna(value=np.mean(df['column_name']), inplace=True)
- Dropping Columns with High NaN Values: If a column has a significant number of NaN values and is not essential for analysis, you might choose to drop it.
# Drop columns with more than 50% NaN values
threshold = len(df) * 0.5 # define your threshold
df.dropna(thresh=threshold, axis=1, inplace=True)
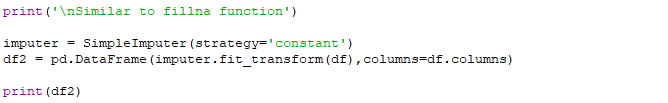
- Imputation: Another approach is to use statistical methods to impute NaN values based on other values in the dataset.
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
# Impute NaN values using mean strategy
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='mean')
imputed_df = pd.DataFrame(imputer.fit_transform(df), columns=df.columns)
- Handling Categorical Data: For categorical data, you might replace NaN values with the mode (most frequent value) of the respective column.
# Fill NaN values in categorical column with the mode
df['categorical_column'].fillna(df['categorical_column'].mode()[0], inplace=True)
Overall, we need to assess the impact of our chosen method on the dataset and the analysis we are performing. The choice of method depends on the nature of our data, the amount of missing data, and the analysis we intend to perform.
=================================================
Handle NaN value in DataFrame: code:

Output:

=================================================
Change data format, print head, print statistic summary of the data, replace empty cells with anything, sort/group columns: code:

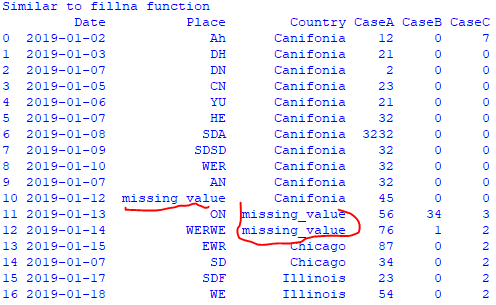
Input:

Output:



===================================================
Machine learning: KNN algorithm: code:


Input:

Output:

|