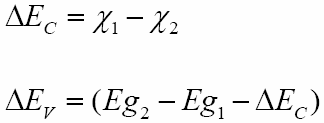|
|
Heterojunction
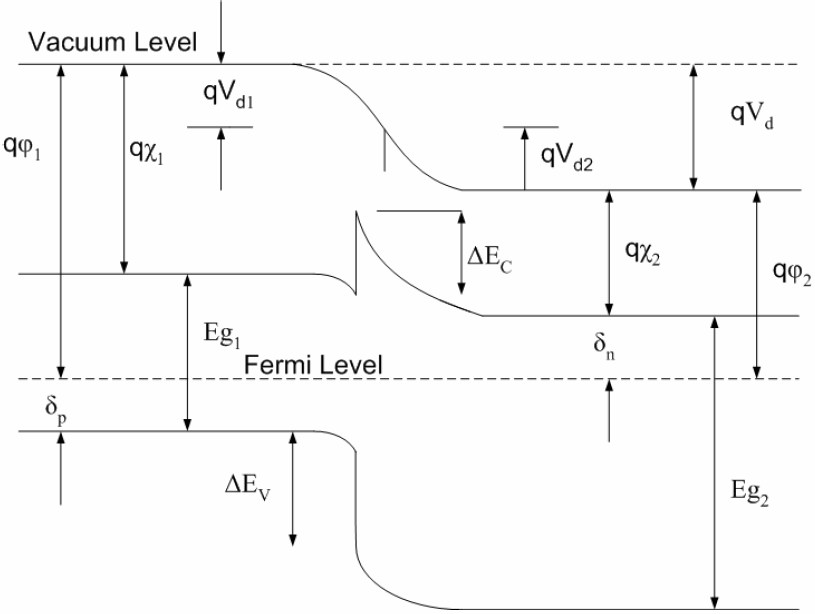
A heterojunction is an electronic junction formed at the boundary between two materials with different atomic or alloy compositions. The energy band diagram of two semiconductor materials prior to forming a junction is shown below:
The two semiconductors have different bandgaps Eg1 and Eg2, different work functions Fm1 and Fm2, different electron affinities x1 and x2 and different permittivities e1 and e2. The energy band diagram of a heterojunction is shown below:
The band discontinuities are given by
Contact us: Feedback Other readings: |
|
||||||||
|
Copyright (C) 2006 GlobalSino, All Rights Reserved
|