Cell Array MAT in DRAM - Integrated Circuits and Materials - - An Online Book - |
||||||||
| Integrated Circuits and Materials http://www.globalsino.com/ICsAndMaterials/ | ||||||||
| Chapter/Index: Introduction | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Appendix | ||||||||
================================================================================= In DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), a "mat" refers to a subarray or a smaller array within the larger DRAM chip. Here are some details about what a mat is and its significance in DRAM design:
Consider a DRAM chip with multiple banks, where each bank contains several mats. When a read or write operation is initiated, the memory controller selects the appropriate bank and mat, and then accesses the specific row and column within the selected mat as shown in Figure 2376a.
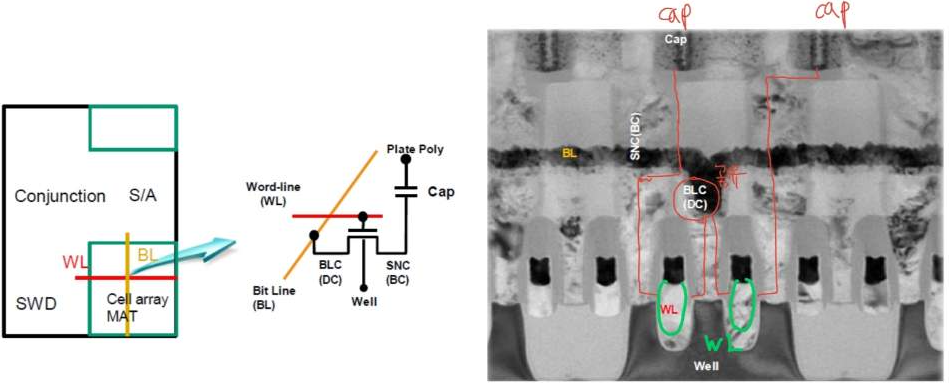
Figure 2376a. Visual representation of banks, mats, and rows. Figure 2376b shows DRAM 8F2 cell structure:
Figure 2376b. DRAM 8F2 cell structure. [1] In the DRAM bank organization shown in Figure 2376c, a DRAM bank is divided into multiple subarrays [3, 4, 5]. Each subarray comprises mul- tiple wordline drivers and sense ampliers (SAs). Subarrays are further divided into DRAM MATs. DRAM MATs are separated from each other by wordline (WL) drivers that are activated to drive a DRAM wordline within the DRAM MAT. In a DRAM MAT, DRAM cells are organized into a two-dimensional structure over bitlines and wordlines. The set of cells over the same wordline forms a DRAM row.
Figure 2376c. DRAM subarray, MAT, row and cell organization. [2] Figure 2376c shows a DRAM MAT with the hierarchical wordline design. In the hierarchical wordline design, a DRAM row address is partitioned into two pieces. The higher-order bits of the row address are used to select and activate a master wordline (MWL). The MWL is connected to four local wordline (LWL) drivers (D0, D1, D2, D3 in Figure 3) that are used to activate four consecutive DRAM rows in a MAT. The least significant two bits of the row address are used to assert one of the four LWL select lines (S0 to S3) to enable an LWL driver and finally activate a DRAM row. An activated MWL potentially drives four consecutive LWLs that form a segment. We hypothesize that the QUAC command sequence (ACT-PRE-ACT) asserts S0 to S3 approximately at the same time, resulting in the simultaneous activation of four consecutive DRAM rows.
Figure 2376c. DRAM MAT with hierarchical wordlines. [2]
============================================
[1] https://blog.naver.com/minky0118/221860772321.
|
||||||||
| ================================================================================= | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||