=================================================================================
The dielectric properties of the films are related to the degree of crystallinity, crystal structure, crystallographic orientation, as well as their stoichiometric composition.
| Table 2077. Static or low-frequency dielectric constant (K), band gap energies, and conduction band (CB) offsets of the gate dielectrics on Si (silicon) substrate. |
Gate dielectrics |
K |
Band gap energy (eV) |
CB offsets (eV) |
a-LaAlO3 |
30 |
5.6 |
1.8 |
Aerogels |
~1.01 ~ 2.0 |
|
|
Ag |
-30 |
|
|
Al |
-60 |
|
|
Al2O3 |
9 |
8.8 |
2.8 |
Au |
-28 |
|
|
Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 |
130–300 |
|
|
CaCu3Ti4O12 |
6.81×104 |
|
|
Ca1–xLaxCu3Ti4O12 |
3000 |
|
|
| Cr |
0 |
|
|
Cu |
-28 |
|
|
CuPc |
2.1 |
|
|
Dry air |
1 |
|
|
Epoxy mold compound (EMC) |
4 |
|
|
HfO2 |
20-25 |
5.8 |
1.4 |
HfSiO4 |
11 |
6.5 |
1.8 |
Ni |
-15 |
|
|
La2O3 |
30 |
6 |
2.3 |
Polymers |
~1.9 ~ 2.9 |
|
|
Si |
|
1.1 |
|
SiO2 |
3.9 |
9 |
3.2 |
SrTiO3 |
2000 |
3.2 |
0 |
Si3N4 |
7-8 |
5.3 |
2.4 |
SrOx |
13.3 |
|
|
Ta2O5 |
22 |
4.4 |
0.35 |
TiO2 |
30 ~ 170, depending on crystal structure and orientation |
3.5 |
0 |
TiN |
-2.3 + 4.8i [1]
|
|
|
W |
0 |
|
|
Vacuum* |
1 |
|
|
Y2O3 |
15 |
6 |
2.3 |
ZrO2 |
25 ~ 46 (tetragonal) |
5.8 |
1.5 |
Metals |
Negative |
|
|
| * ε0 = 8.854 × 10−12 C/Vm |
Figure 2077 shows the distribution of band gap versus dielectric constant of dielectrics.
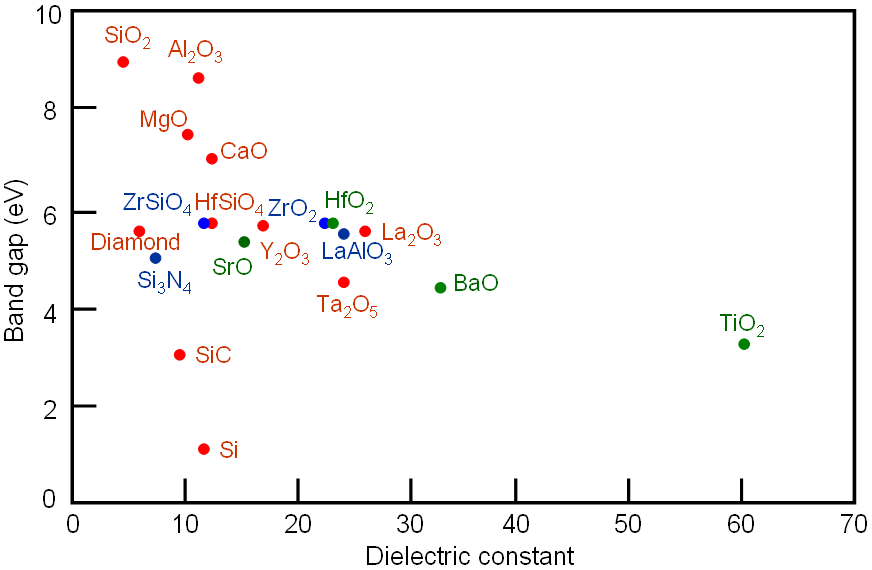
Figure 2077. Distribution of band gap versus dielectric constant of dielectrics.
[1] E. D. Palik, Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids II (Academic, San Diego, Calif., 1991).
|