|
|
Effect of Amorphous Layer on Contrast of HRSEM Images
- Practical Electron Microscopy and Database -
- An Online Book -
|
|
https://www.globalsino.com/EM/
|
|
This book (Practical Electron Microscopy and Database) is a reference for TEM and SEM students, operators, engineers, technicians, managers, and researchers.
|
=================================================================================
Inada and Zhu, et al. [1] obtained high-resolution secondary electron microscopy (HRSEM) images of silicon (Si) TEM specimens along (110) direction, taken in a HD 2700C electron microscope using a 0.1 nm scanning probe
with a Cs corrector. Figure 2940 shows the lattice fringes of a HRSEM image taken from a TEM specimen covered with a 3 nm amorphous layer induced by FIB specimen preparation. The speckle contrast is due to variation in thickness of the 3-nm amorphous layer. They also found visible lattice fringes in very low intensity for a specimen with an amorphous Si layer of 8 nm thick, while there was only a little atomic contrast in the (110) lattice for a specimen with an amorphous Si layer of 28 nm thick.
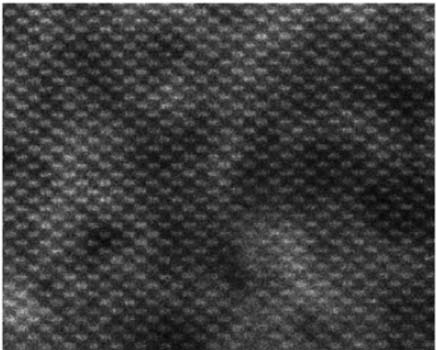
Figure 2940. HRSEM image of a Si TEM specimen along (110) direction. Adapted from [1]
[1] H. Inada, D.Su, R. F. Egerton, M.Konno, L.Wu, J.Ciston, J.Wall, Y.Zhu, Atomic imaging using secondary electrons in a scanning transmission electron microscope: Experimental observations and possible mechanisms, Ultramicroscopy 111(2011)865–876.
|
=================================================================================
The book author (Yougui Liao) welcomes your comments, suggestions, and corrections, please click here for submission. You can click How to Cite This Book to cite this book. If you let book author know once you have cited this book, the brief information of your publication will appear on the “Times Cited” page.
|
|
