=================================================================================
Figure 2695a illustrates the comparison of the main contrasts in both CTEM and STEM modes.
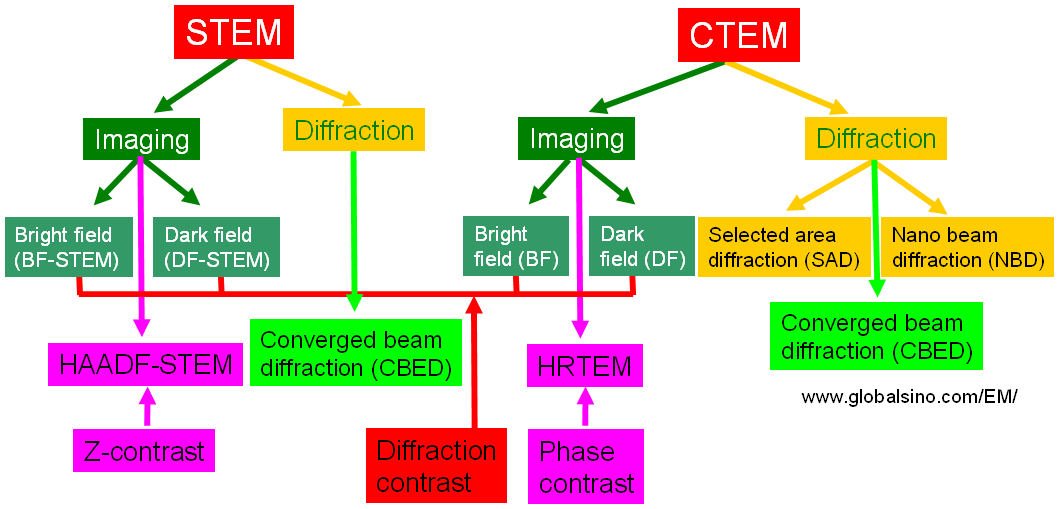
Figure 2695a. Comparison of the main contrasts in both CTEM and STEM modes.
The probe formation in NBD measurement is different from other TEM modes. The schematic illustrations in Figure 2695b show the convergent illumination configurations of various modes in TEMs. In the CTEM condition in Figure 2695b (a), the condenser mini-lens (CM lens) is strongly excited, and incident electrons are focused on the pre-focal point of the objective pre-field, resulting in a parallel illumination on a wide area on the specimen and providing highly coherent electron illumination. In the EDS condition in Figure 2695b (b), the CM lens is turned off and the incident electrons are focused on the specimen by the objective pre-field, resulting in a small-probe illumination. In this case, the illumination angle (α1) is large so that high beam intensity is obtained for a small area in the analytical EDS method. In the NBD mode in Figure 2695b (c), a smaller condenser aperture is used to form a smaller illumination angle (α2). Therefore, a small-diameter probe with relatively high coherence in the illumination is achieved. In the illumination condition in Figure 2695b (c), the illumination angle (α) with a constant probe size can be changed by changing the excitations of the condenser lenses and the CM lens to obtain the incident illumination to form ideal convergent beam electron diffraction (CBED) patterns.
Figure 2695b. Convergent illumination configurations: (a) CTEM mode, (b) EDS mode and (c) NBD mode.
For nanoparticles, the combined TEM-NBD techniques are capable of unambiguous identification of a phase as small as 1 nm in size. However, the sensitivity compares favourably with conventional selected area electron diffraction (SAED) and microdiffraction which correlate diffraction patterns with areas about 500 and 100 nm in size in the specimens, respectively.
|