=================================================================================
Modern SEM instruments use in-lens (frequently called through-the lens, immersion-lens, or upper) SE detectors and the specimen is often immersed in the magnetic (or electric) field of the final lens. Electrostatic deflectors permit selection of the SE involved in the image-forming system. In-lens SEM detectors mostly collect SE1 secondary electrons as shown in Figure 4603a. The SE1s are generated by direct interaction with the incident (primary) electron beam and therefore carry the highest spatial resolution information.
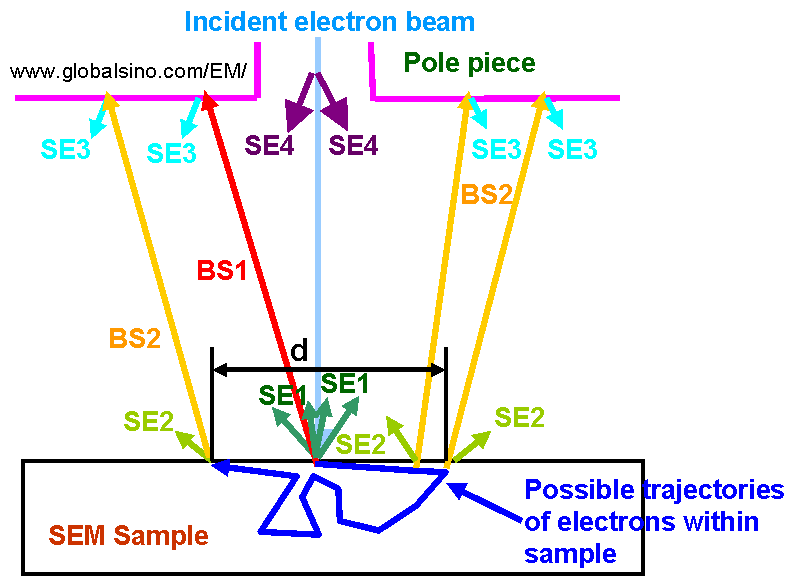
Figure 4603a. Schematic of generation of various electrons including
secondary electrons and backscattered electrons.
In order to enhance the effect of SE1 in-lens imaging, the energy of the primary beam should be reduced as discussed earlier. Figure 4603b shows the positions of in-lens detector and the lateral detector in the sample chamber. A DC (direct current) bias of about 10 kV is used to enhance the detection efficiency of the SEs. Note that the single-pole snorkel objective lens shown in Figure 4603b produces a strong magnetic field that extends from the polepiece directly to the SEM specimen. This type of lenses is a compromise between the aberrations of immersion lens and pinhole lens but accommodate large specimens similar to those in the pinhole lens SEMs.
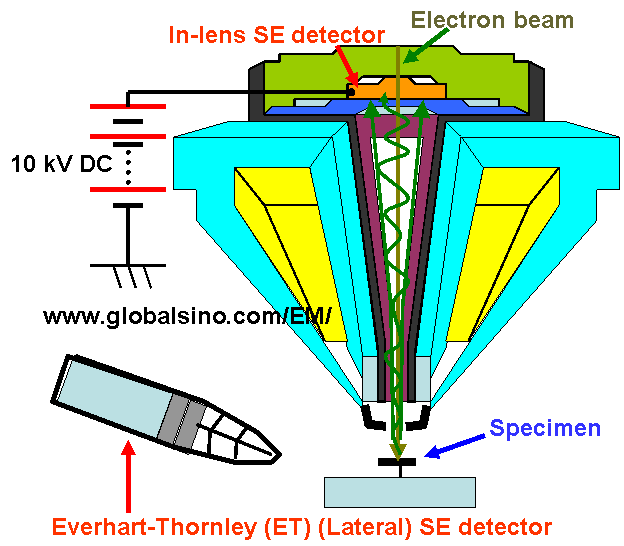
Figure 4603b. Positions of in-lens detector and the lateral detector in the sample chamber.
Furthermore, the immersion lens (in-lens) acts as a perfect electron trap for the EDS detector without compromising the collection geometry of EDS or image resolution of SEM.
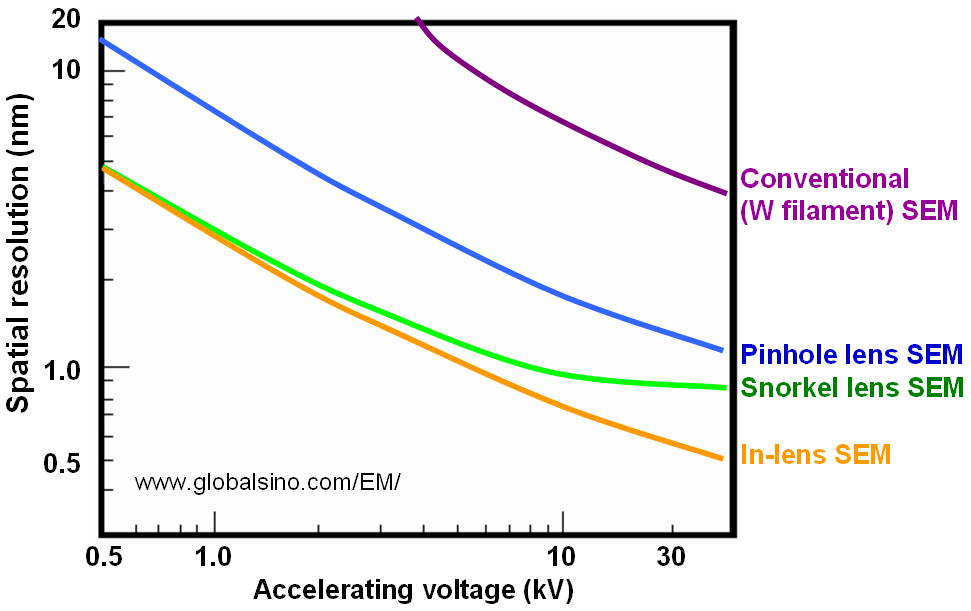
Figure 4603c shows the schematic illustration of spatial resolutions of SEMs with various lenses, including conventional W (tungsten) filament SEMs, pinhole lens, snorkel lens, and in-lens. The best resolution can be obtained by in-lens SEMs.
 |
|
Figure 4603c. Schematic illustration of spatial resolutions of SEMs with various lenses. |
|


