=================================================================================
X-ray absorption and fluorescence normally exist in EDS measurements in EMs. Those effects not only induce analysis artifact but also affect the spatial resolution of EDS measurements. The EDS analysis artifact is very significant in thick and bulk samples, while they can, to a first approximation, be ignored in thin samples, e.g. very thin TEM films. Note that we need to especially pay attention to this type of artifact when we are working on wedge-shaped TEM samples such as those prepared by angled-FIB or ion milling techniques, or working on particles. Figure 3781 shows the EDS measurements of a Ti(titanium)-doped wedge-shaped sample and an embedded TixOy particle. It is not necessary that the Ti concentration at location A is higher than that at location B even though the Ti peak at location A is much higher than that at location B as shown in Figure3781 (a). The high signal can be obtained just because the location A is thicker. Similarly, for the measurement of the embedded TixOy particle, it is not necessary that the Ti concentration at location C is higher than that at location D because of the same reason. This principle can also be applied to other elements.
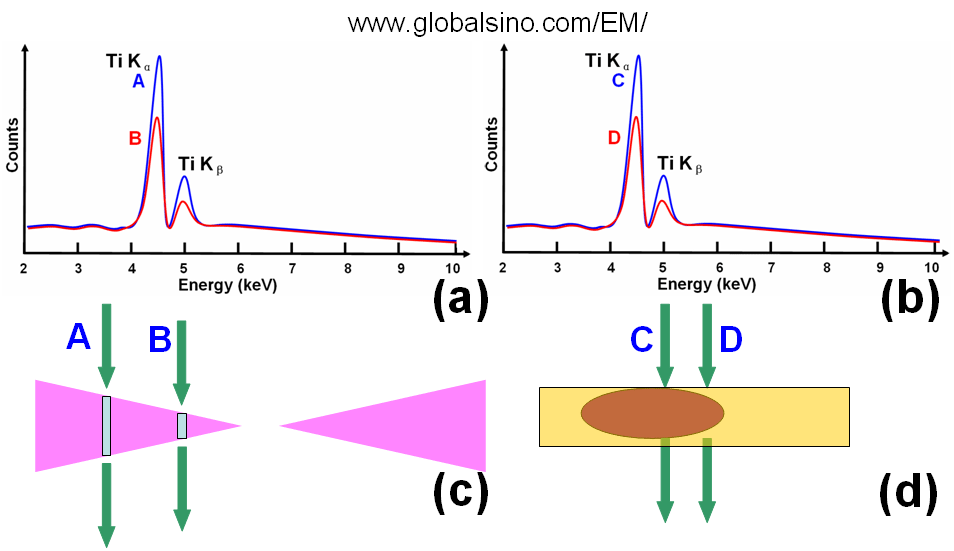
Figure 3781. Schematic illustration of EDS measurements of a Ti-doped wedge-shaped samples
and a TixOy particle. It is not correct to compare the absolute Ti concentration between location
A and B and between C and D just based on the strength of the Ti peaks.
When the X-ray absorption is significant, especially for SEM-EDS measurements on bulk samples, the shape of the depth distribution of X-ray production is crucial, and thus ZAF and Phi–Rho–Z models should be used. However, the mass absorption coefficients are still problematic because significant uncertainties exist even in absorption-corrected ZAF and Phi–Rho–Z models.
|