=================================================================================
Table 3553a and Figure 3553 show the monoclinic crystal systems and the schematic illustration of the monoclinic lattices, respectively.
Table 3553a. Monoclinic crystal systems.
Crystal
family |
Crystal
system |
Required
symmetries
of point group |
Point
group |
Space
group |
Bravais
lattices |
Lattice
system |
Monoclinic
|
1 two-fold axis of rotation or 1 mirror plane |
3
|
13
|
2
|
Monoclinic |
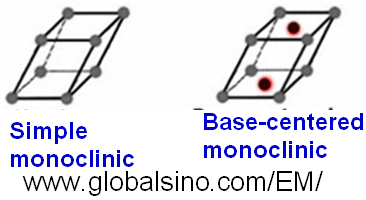
Figure 3553. Schematic illustrations of the Bravais
lattices of monoclinic crystals.
Table 3553b. Relationship between Laue classes and point groups.
| System |
Essential symmetry |
Lattice symmetry |
Laue class (Diffraction symmetry) |
Point Groups (Hermann–Mauguin notation) |
| Triclinic |
None |
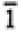 |
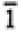 |
1, -1 |
| Monoclinic |
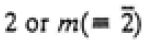 |
2/m |
2/m |
2, m, 2/m |
| Orthorhombic |
222 or 2mm
|
mmm
|
mmm |
222, mm2, mmm |
| Tetragonal |
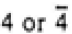 |
4/mmm
|
4/m
|
4, -4, 4/m |
| 4/mmm |
422, -42m, 4mm, 4/mmm |
| Trigonal |
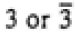 |
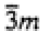 |
3 |
3, -3 |
| -3m1 |
321, 3m1, -3m1 |
| -31m |
312, 31m, -31m |
| Hexagonal |
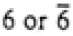 |
6/mmm
|
6/m |
6, -6, 6/m |
| 6/mmm |
622, -62m, 6mm, 6/mmm |
| Cubic |
23 |
m3m
|
m-3 |
23, m-3 |
| m-3m |
432, -43m, m-3m |
For monoclinic structures, the lattice spacing (d-spacing) can be given by, (You can download the excel file for your own calculations)
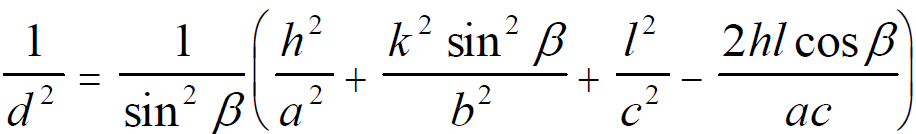 --------------------------------- [3553] --------------------------------- [3553]
where,
a, b and c -- The lattice constants.
h, k, and l -- The Miller indices.
In crystals, anisotropy of many properties clearly arises because the arrangement of their atoms varies in different directions. In general, cubic crystals is less anisotropic than monoclinic ones because of their greater symmetry, for instance, with respect to electrical conductivity. Therefore, cubic crystals do not exhibit electrical polarization when the temperature is changed, so that their pyroelectric effect is isotropic.
Table 3553c. Centrosymmetric, non-centrosymmetric, and chiral space groups for monoclinic crystal systems.
| Crystal system |
Laue group |
Point group |
Space group |
| Monoclinic |
2/m |
2 |
P2, P21, C2 |
| m |
Pm, Pc, Cm, Cc |
| 2/m |
P2/m, P21/m, C2/m, P2/c, P21/c, C2/c |
| Red: chiral; green: non-centrosymmetric; and yellow: centrosymmetric. |
Table 3553d. Other characteristics of monoclinic structures.
Contents |
Page |
| Angles in unit cells |
page3555 |
| Volume of unit cells |
page3033 |
| Bravais lattices |
page4546 |
| Relationship between three-dimensional crystal families, crystal systems, space group, point group, lattice systems and symmetries |
page4549 |
|

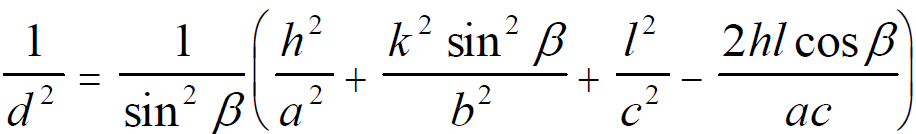 --------------------------------- [3553]
--------------------------------- [3553]