=================================================================================
The passive voltage contrast (PVC) in FIB and SEM can be very complicated if diodes, capacitors and/or transistors are integrated in the analyzing IC device. The factors which affect the imaging contrast of the structure can be, for instance, pn junctions, doping, and thickness and size of capacitor plates.
Figure 3857a shows the PVC (passive voltage contrast) in the contact level of WL (word line) decoder of a DRAM circuit. The p-contacts in n-well and n-/p- well contacts generate the brightest signal. P-contacts in n-well generate the brightest signal because of the forward bias in the pn-junction. The n-contacts in p-well generate the second brightest signal. The gate contacts generate dark signal because they are fully positively charged.
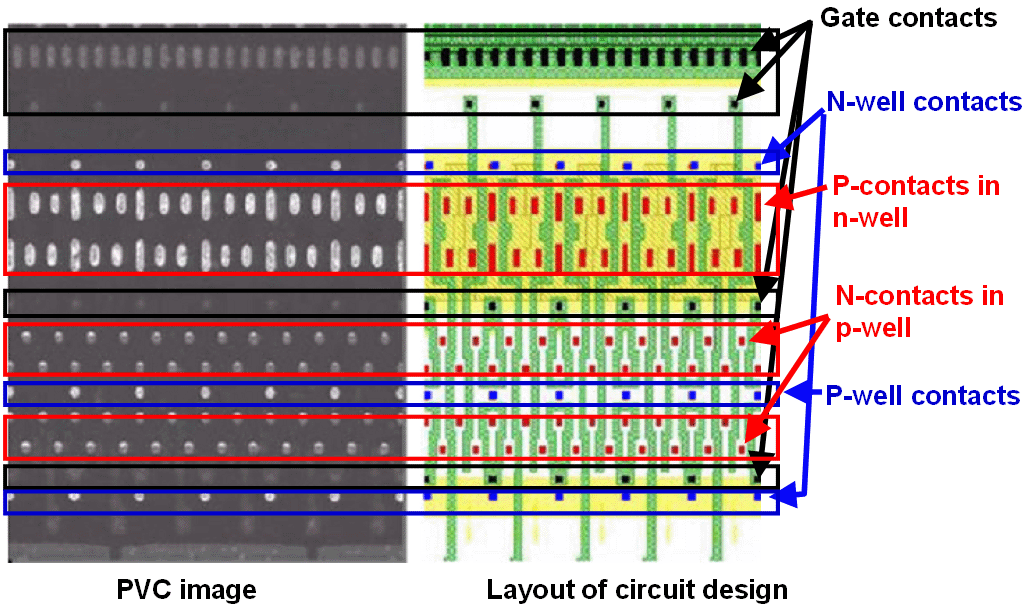
Figure 3857a. The PVC in contact level of WL (word line) decoder of a DRAM circuit. Adapted from [1].
The electrical potential of any observing structure can always be simplified to an equivalent circuit diagram consisting of a capacitance C and a resistance R to ground. The capacitance and resistance can be variable but it is fairly accurate if we just consider them as constants in normal SEM and FIB operation conditions. The net current between the beam-irradiating spot and the ground is the total current (It) of the incident beam and the emitted secondary electrons (SEs). The electrical potential of the observing structure can be modified from the format presented by other authors [1] and be given by,
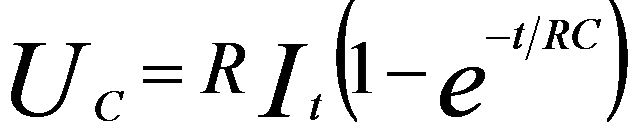 -------------------------- [3857a] -------------------------- [3857a]
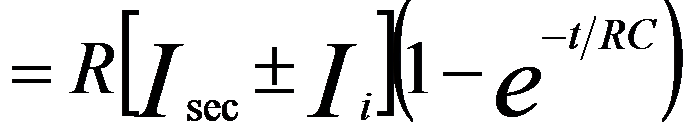 -------------------------- [3857b] -------------------------- [3857b]
“-” is applied when an electron beam is used as the incident beam, while “+” is applied when a positive ion beam is used as the incident beam.
Figure 3857b shows the schematic illustration of the current flows. The inset presents the electrical potential of the observing structure as a function of time. There are two potential thresholds: dark threshold (Ud) and bright threshold (Ub). If the resulted potential is higher than Ud the structure appears dark, while the structure appears bright if the potential is lower than Ub. The tscan is the scanning time of the incident beam.
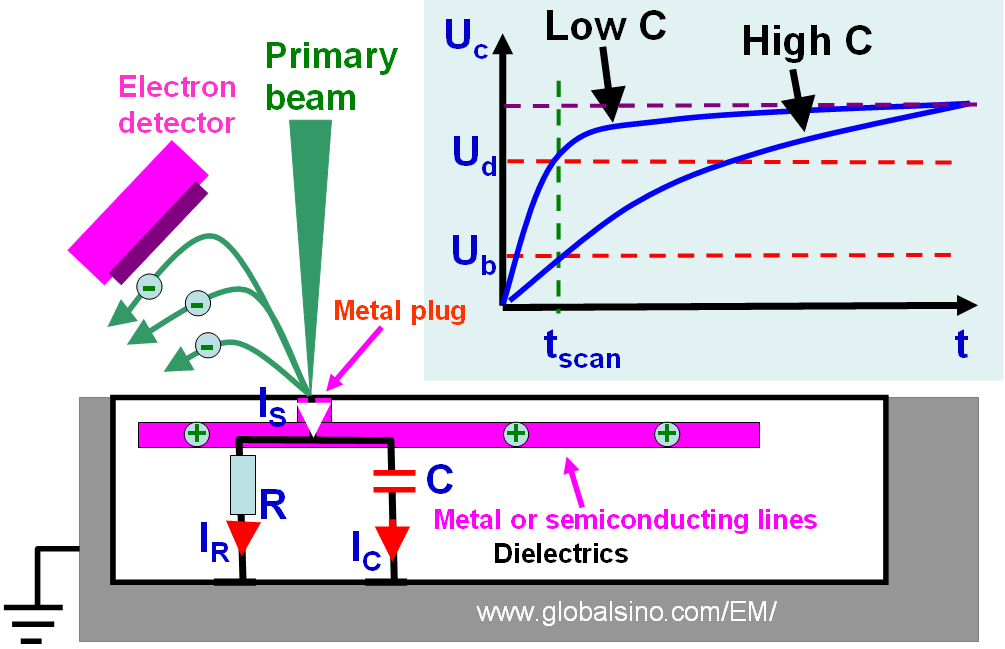
Figure 3857b. Schematic illustration of the current flows of the equivalent circuit diagram. The inset shows
the potential of the observing structure as a function of time.
In the some complicated cases, one possible solution is that we can identify the shorts or openings by comparing a local contrast with each other if the analyzing IC is an array.
[1] Ruediger Rosenkranz, Failure localization with active and passive voltage contrast in FIB and SEM, J Mater Sci: Mater Electron (2011) 22:1523–1535.
|

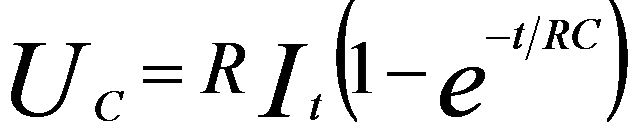 -------------------------- [3857a]
-------------------------- [3857a] 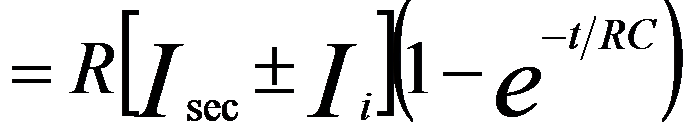 -------------------------- [3857b]
-------------------------- [3857b] 