=================================================================================
Besides the objective lens, intermediate (and/or diffraction) lenses and projector lenses further magnify the electron image and form the final image on the viewing screen.
Figure 1985a shows the comparison of the lens conditions between TEM diffraction and TEM imaging modes. Those two modes are the basic modes in TEM operations. The difference between the two modes may only be the strength of the intermediate lens.
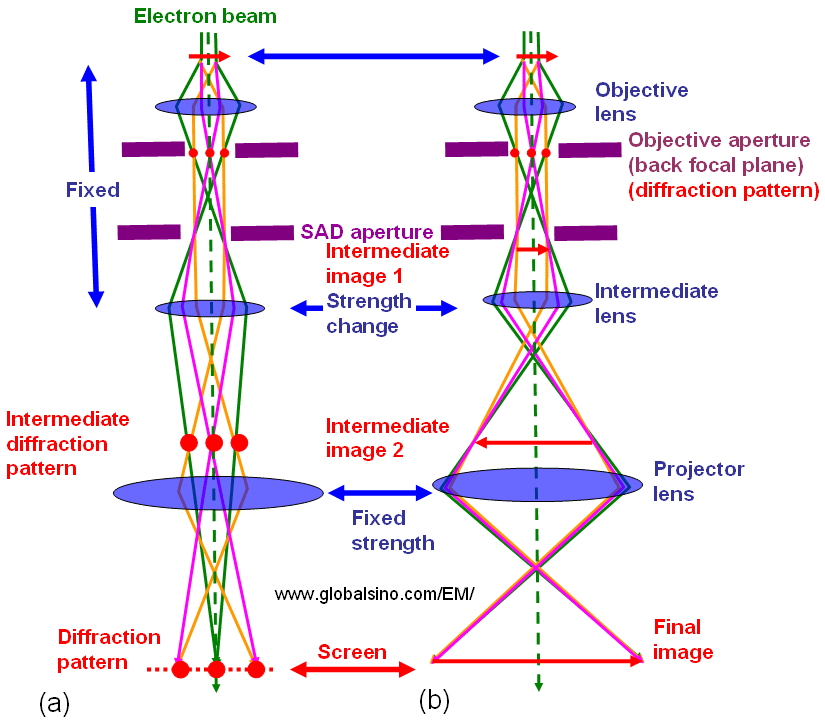
Figure 1985a. Comparison of the lens conditions between TEM diffraction and TEM imaging modes.
Figure 1985b presents more details. Figure 1985b (a) shows the principle of magnifying an image (Normal-Mag mode). A transmitted image of the specimen is first formed and magnified by the objective lens, and then is magnified further by two to four lenses, including an objective lens, intermediate lenses, and a projector lens. As shown in Figure 1985b (b), at extremely low magnification (e.g. used for survey of interest), the image is formed by the OM (objective-mini) lens, intermediate lenses, and projector lens. The Diff mode in Figure 1985b (c)presents an electron diffraction pattern. In the Normal-Mag mode, the focus of the 1st intermediate lens is adjusted to the image plane of the objective lens where a selected area aperture is located. However, in the Diff mode, the focus of the 1st intermediate lens is adjusted at the back focal plane of the objective lens. Table 1985 lists the status of the lenses and apertures in different operation modes.
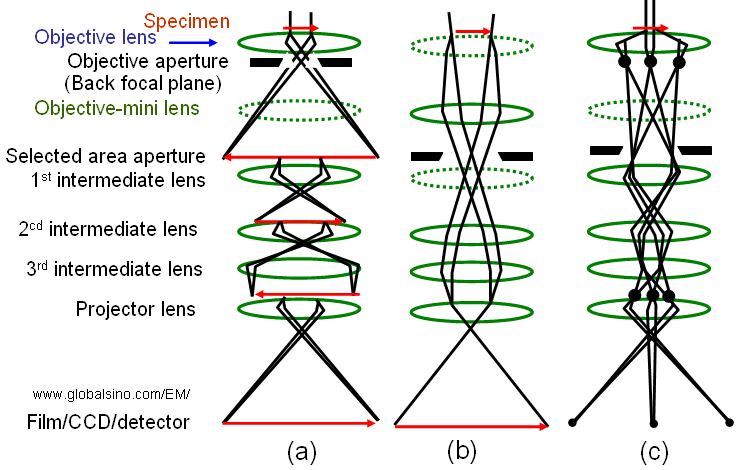
Figure 1985b. (a) Normal-Mag mode, (b) Low-Mag mode, and (c) Diff mode. The dashed-lenses are turned off in the relevant operation mode.
Table 1985. Status of the lenses and apertures in different operation modes*.
Lens |
|
|
|
|
On |
Off |
On |
Objective aperture (back focal plane)
|
Normally use |
Normally not use |
Normally not use |
|
Off |
On |
Off |
|
Normally not use |
Either use or not use |
Either use or not use |
Focus of 1st intermediate lens |
At the image plane of the objective lens |
- |
At the back focal plane of the objective lens |
|
On |
Off |
On |
|
On |
On |
On |
|
On |
On |
On |
|
On |
On |
On |
* "Normal-Mag mode" includes normal and high magnifications for HRTEM; "Low-Mag mode" includes very low magnifications, which is used for specimen survey; and "Diff mode" is for electron diffraction analysis. |
There are mainly two steps to correct the astigmatisms in TEMs:
i) Correct the astigmatisms of the diffraction (inter-mediate, IL) and condenser (CL) lenses. Before the astigmatism correction for objective lens (OL) , the IL and CL astigmatisms should be corrected. The CL astigmatism must especially be corrected (without objective aperture) to ensure the proper correction of the OL astigmatism.
ii) Correct the OL astigmatism.
To have a camera length exactly as labeled in the instrument, some key points need to be satisfied as follows:
i) The specimen should be placed exactly at the Eucentric height in the objective lens.
ii) A parallel electron beam should be employed.
iii) The focus of the objective lens should be exactly adjusted to the focus position.
iv) The focus of the first intermediate (with “Diff focus” knob) should be adjusted at the back focal plane of the objective lens.
|
