=================================================================================
Table 3713. List of notations in the book.
| Symbols |
Meanings |
Examples |
| a |
Diameter of the objective aperture |
|
| a |
A lattice or cell parameter: length of a basis vector, length of a cell edge |
|
| a' |
A new basis vector after a transformation of the coordinate system |
|
a (or 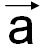 ) ) |
One of the basis vectors of direct lattice |
|
| a* |
Length of a basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
| a* |
A basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
| A |
Thickness of the crystal in the TEM specimen |
page3769 |
| A |
Atomic weight of the atoms in the specimen |
page2673 |
| A(k) |
The aperture function describing the effect of the objective aperture |
page3732 |
| A(u) |
Aperture function |
page4236 |
| Ad |
Dimensionless atomic mass . |
page2673 |
| AS |
Surface area of a sphere |
page2671, page4631 |
| b |
A lattice or cell parameter: length of a basis vector, length of a cell edge |
page3464 |
b (or 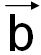 ) ) |
One of the basis vectors of direct lattice: Burgers vector |
|
| b' |
A new basis vector after a transformation of the coordinate system |
|
| b* |
Length of a basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
| b* |
A basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
c (or 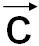 ) ) |
One of the basis vectors of direct lattice |
|
| c |
A lattice or cell parameter: length of a basis vector, length of a cell edge |
|
| c' |
A new basis vector after a transformation of the coordinate system |
|
| c* |
Length of a basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
| c* |
A basis vector of reciprocal lattice |
|
| Cc |
Chromatic aberration coefficient |
page4165 |
| Cn |
Rotation axis in crystallography (1, 2, 3, 4 and 6) |
page1622 |
| Cs |
Spherical aberration of the objective lens |
page1715 |
| C1s |
Excitation coefficient for plane wave incidence |
page4217 |
| d |
Diameter of TEM specimen over which the illumination is coherent |
page1708 |
| D(k) |
Envelope function |
page3879 |
| dhkl |
Lattice-plane spacing of the (hkl) planes, i.e. interplanar distance of neighbouring net planes (hkl) |
|
| e |
Elementary charge |
|
| EL2,3 |
Si L2,3 energy loss onset of the silicon compounds |
page3441 |
| E(u) |
Envelope functions, including Es and Ec |
page4236 |
| Et(|g|) or Et(u) |
Temporal-coherence envelope function |
page4236, page4165 |
| E0 |
Incident electron energy |
page4217 |
| E1s |
The energy of the lowest energy bound state |
page4217 |
| En |
(Euclidean) point space of dimension n |
|
| ΔE |
Energy range of the PEEL spectra |
page3384 |
| Es(|g|) |
Spatial-coherence envelope function |
page4236, page4153 |
| f(θ) |
Atomic scattering factor |
page1421 |
| fe(s) |
Atomic scattering factor for electrons |
|
| F(g) or Fhkl |
Structure factor of the cell, corresponding to the Bragg reflection hkl |
|
| fX |
Atomic scattering factor for x-rays |
|
| F |
Fourier transform |
|
| F-1 |
Inverse Fourier transform |
|
| |F(hkl)|; or |F| |
Modulus of the structure factor F(hkl) |
|
| g |
Spatial frequency |
page1715 |
| |g| |
The spatial frequency |
page3732 |
| gij |
Element of metric tensor |
|
| ghkl |
Reciprocal-space vector for the planes with indices hkl |
|
| G |
Metric tensor of direct lattice |
|
| G* |
Metric tensor of reciprocal lattice |
|
| h |
Planck’s constant |
|
| h |
Reciprocal-lattice vector |
|
| hkl |
Miller indices: indices of the Bragg reflection (Laue indices) from the set of parellel equidistant net planes (hkl) |
page2506 |
| hkl |
Coordinates of a reciprocal-lattice point, coefficients of reciprocal-lattice vector r* |
|
| (hkil) |
Bravais-Miller indices: indices of a crystal face, or of a single net plane, for the hexagonal axes a1, a2, a3, c |
|
| (hkl) |
Miller indices: indices of a crystal face, or of a single net plane |
page2506 |
| {hkl} |
Indices of a set of all symmetrically equivalent crystal faces or net planes, i.e., the family of all the planes that are equivalent to (hkl) by the symmetry of the lattice |
page2506 |
| {hkil} |
Indices of a set of all symmetrically equivalent crsytal faces or net planes for the hexagonal axes a1, a2, a3, c |
|
| [hkl] |
A direction that denotes the direction in the basis of the direct lattice vectors instead of the reciprocal lattice |
page2506 |
| <hkl> |
A family of the directions that are equivalent to [hkl] by symmetry |
page2506 |
| i |
Center of inversion (center of symmetry) |
page1614 |
| I0 |
Objective lens current |
page4165 |
| I0 |
Intensity of the incident electron beam, |
page3769 |
| k |
The reciprocal space vector |
page3732 |
| L |
Vector lattice |
|
| m |
Mirror planes in crystals |
page1620 |
| m |
Relativistic electron mass |
|
| m0 |
Electron rest mass |
page4787 |
| mp |
Proton mass |
page2673 |
| M |
Symmetry operation or motion |
|
| n |
Dimension of a space |
|
| N |
Atomic density |
page2673 |
| NA |
Avogadro’s number |
page4475, page2673 |
| p(r) |
Point spread
function of a system |
page4907 |
| Puvw |
Probability of seeing a family of zone axes <uvw> |
|
| P(xyz) |
Patterson function at the point x,y,z |
|
| qe(r) |
Specimen transmission function |
|
| Q |
Probability of scattering an electron |
page2673 |
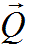 |
Scattering vector |
page1421 |
| r |
Length of the position vector r (or 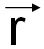 ) ) |
|
r (or 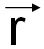 ) ) |
Position vector of a point or an atom: The real space coordinates, three-dimensional position vector in direct space |
page3732 |
| r* |
Reciprocal-lattice vector |
|
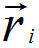 |
Position of atom i |
page1421 |
| s |
|g|/2 |
|
| S |
Illuminating area by the incident electron beam |
page3769 |
| S |
Point spread function (PSF) of a system |
page2621 |
| t |
Length of a translation vector t |
|
| t |
Translation vector |
|
| t(r) |
Spread function of the objective lens |
|
| T(u) |
Microscope transfer function |
|
| u |
Spatial frequency |
page3699 |
| u |
The reciprocal space coordinates |
page3732 |
| u |
Two-dimensional vector in the back focal plane of the objective lens |
|
| u |
Vector with integral coefficients |
|
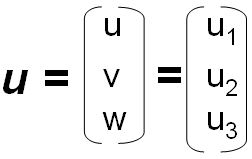 |
Column of integral point coordinates or vector coefficients |
|
| V |
Cell volume of direct lattice |
|
| V0 |
Accelerating voltage of the electrons |
page4165 |
| Vt |
The projected potential |
page4173 |
| Vn |
Vector space of dimension n |
|
| V* |
Cell volume of reciprocal lattice |
|
| w |
Weighting factor |
|
| W |
Symmetry operation or motion |
|
| (W,w) |
Symmetry operation W, described by an (n x n) matrix W and an (n x 1) column w |
|
| X |
Point |
|
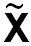 |
Image of a point X after a symmetry operation |
|
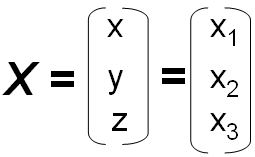 |
Column of point coordinates or vector coefficients |
|
| xa |
A component of the position vector r (or 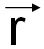 ) ) |
|
| Xkl |
Complex Fourier coefficient of the pixel at (k, l) |
|
| yb |
A component of the position vector r (or 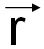 ) ) |
|
| z |
Crystal thickness |
page4217 |
| Z |
Average atomic number |
page4476 |
| zc |
A component of the position vector r (or 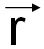 ) ) |
|
| r'; x', y', z'; or xi' |
Position vector and point coordinates after a transformation of a coordinate system |
|
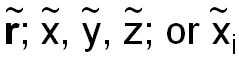 |
New position vector and point coordinates after a symmetry operation |
|
| u, v, w; or ui |
Integers, coordinates of a (primitive) lattice point; coefficients of vector u |
|
| [uvw] |
Indices of a lattice direction or zone axis |
|
| <uvw> |
Indices of a set of all symmetrically equivalent lattice directions |
|
| x, y, z; or xi |
Coordinates of a point (location of an atom) expressed in units of a, b, c; coordinates of end point of position vector r (or 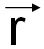 ); coefficients of position vector r (or ); coefficients of position vector r (or 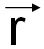 ). ).
|
|
| ξ |
sense vector |
page3461 |
| ξhkl |
Extinction distance |
page3769/page4134 |
| φ(r) |
Electrostatic potential |
|
| Φhkl |
Fourier coefficients of an electrostatic potential. |
page3880 |
| ΦP |
Fourier transform of the projected electrostatic potential |
|
| Ψexit |
Exit wave function from TEM Specimen |
page4217 |
| ψillum |
Illumination wave function |
page3732 |
| ψi(r) |
Image wave function |
page3732 |
| ψo(r) |
Object wave function (in real space) |
page3732 |
| ψo(u) |
Object wave function (in reciprocal space) |
page3732 |
| Ψo,s |
Wave function of scattered electrons |
page4217 |
| Φhkl |
Fourier coefficients of an electrostatic potential |
page3769 |
| Φ1s(r) |
The lowest energy bound state of the atom column |
page4217 |
| α |
A lattice or cell parameter: an interaxial (lattice) angle b ^ c |
|
| α |
Electron beam convergence |
page3879 |
| α* |
An interaxial (lattice) angle of reciprocal lattice b* ^ c* |
|
| αmax |
�Visibility band half-width |
|
| α(hkl); or α |
Phase angle of the structure factor F(hkl) |
|
| ρ |
Density of the material (g/cm3). |
page4475, page2673 |
| ρ(xyz) |
Electron density at the point x,y,z |
|
| β |
A lattice or cell parameter: an interaxial (lattice) angle c ^ a |
|
| β |
Brightness of electron beam |
page4961 |
| β |
Collection angle of EELS |
page3384 |
| β2 |
Collection angle (mrad) |
page4476 |
| β* |
An interaxial (lattice) angle of reciprocal lattice c* ^ a* |
|
| γ |
A lattice or cell parameter: an interaxial (lattice) angle a ^ b |
|
| γ* |
An interaxial (lattice) angle of reciprocal lattice a* ^ b* |
|
| θ |
The scattering angle |
page3732 |
| σ |
An interaction constant |
page4173 |
| σ |
Mirror planes in crystals |
page1620 |
| σ |
Cross section (of an incident electron interacting with an atom) |
page2673 |
| σT |
Total scattering cross sectoin (including both elastic and inelastic scatterings, i.e. σelastic + σinelastic) for an isolated atom, |
page2673 |
| Θ, or θ |
Half of the angle between the transmitted and scattered electron beams |
page3769 |
| ϕ |
Phase |
|
| λ |
Electron wavelength |
page4787 |
| λ |
Mean free path (of an incident electron interacting with an atom) |
page2673 |
| χ |
The phase shift from defocus and spherical aberration, phase-distortion function |
page3732 |
| Δ |
Defocus spread |
page3879 |
| Δ |
Difference parameter |
|
| Δf |
Objective lens defocus |
|
| Δdc |
Chromatic broadening |
page3384 |
| ΔEL2,3 |
Separation of the L3 and L2 peak maxima |
page4770 |
| ΔEL2,3 |
Chemical shift of Si L2,3 from that of pure silicon |
page3441 |
| Δf |
Defocus |
page1715 |
| δE |
Intrinsic energy spread of E0 |
page4165 |
| Ω |
Solid angle subtended by the intersection of two visibility bands |
|
| Γ |
Visibility factor in calculating lattice-fringe visibility band half-widths |
|
| δ |
Dirac delta function |
|
| τ |
A relativistic correction factor |
page4476 |
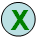 |
into the page |
page4315 |
| [ ] |
An orientation of a crystal |
|
| [ ] |
A zone axis |
|
| < > |
A group of orientations of a crystal |
|
| ( ) |
A crystalline plane |
|
| { } |
A group of planes of a crystal |
|
| / |
Indicates parallel symmetry elements |
page2982 |
| Schoenflies notation |
|
page1677 |