=================================================================================
The incident Ga ions may be backscattered during FIB milling as shown in Table 1168. Note that the backscattered Ga ions normally do not contribute to the spttering yield. Therefore, only the remaining Ga ions will produce sputtered atoms from the sample. In general, materials with a higher sputtering yield, have a higher backscattering yield of incident ions. [1]
| Table 1168. Examples of fraction of backscattered Ga ion in FIB milling and SIMS measurement. |
| Material or atomic number |
|
Fraction of backscattered Ga ion |
Note |
| Voltage |
5 kV |
5 kV |
30 kV |
30 kV |
|
| Angle |
0 degree |
88 degrees |
0 degree |
88 degrees |
|
| 1 |
H |
0.00 |
0.36 |
0.00 |
0.32 |
|
| 2 |
He |
0.00 |
0.51 |
0.00 |
0.48 |
|
| 3 |
Li |
0.00 |
0.62 |
0.00 |
0.55 |
|
| 4 |
Be |
0.00 |
0.65 |
0.00 |
0.60 |
|
| 5 |
B |
0.00 |
0.61 |
0.00 |
0.63 |
|
| 6 |
C |
0.00 |
0.64 |
0.00 |
0.61 |
|
| 7 |
N |
0.00 |
0.63 |
0.00 |
0.57 |
|
| 8 |
O |
0.00 |
0.58 |
0.00 |
0.64 |
|
| 9 |
F |
0.00 |
0.64 |
0.00 |
0.56 |
|
| 10 |
Ne |
0.00 |
0.68 |
0.00 |
0.61 |
|
| 11 |
Na |
0.00 |
0.68 |
0.00 |
0.61 |
|
| 12 |
Mg |
0.00 |
0.69 |
0.00 |
0.56 |
|
| 13 |
Al |
0.00 |
0.60 |
0.00 |
0.56 |
|
| 14 |
Si |
0.00 |
0.73 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
|
| 15 |
P |
0.00 |
0.66 |
0.00 |
0.52 |
|
| 16 |
S |
0.00 |
0.73 |
0.00 |
0.63 |
|
| 17 |
Cl |
0.00 |
0.70 |
0.00 |
0.61 |
|
| 18 |
Ar |
0.00 |
0.70 |
0.00 |
0.67 |
|
| 19 |
K |
0.00 |
0.62 |
0.00 |
0.66 |
|
| 20 |
Ca |
0.00 |
0.67 |
0.00 |
0.74 |
|
| 21 |
Sc |
0.00 |
0.72 |
0.00 |
0.59 |
|
| 22 |
Ti |
0.00 |
0.73 |
0.00 |
0.73 |
|
| 23 |
V |
0.00 |
0.66 |
0.00 |
0.68 |
|
| 24 |
Cr |
0.00 |
0.67 |
0.01 |
0.69 |
|
| 25 |
Mn |
0.00 |
0.68 |
0.01 |
0.62 |
|
| 26 |
Fe |
0.00 |
0.69 |
0.00 |
0.65 |
|
| 27 |
Co |
0.00 |
0.73 |
0.01 |
0.69 |
|
| 28 |
Ni |
0.00 |
0.72 |
0.00 |
0.69 |
|
| 29 |
Cu |
0.00 |
0.67 |
0.01 |
0.68 |
|
| 30 |
Zn |
0.00 |
0.71 |
0.00 |
0.67 |
|
| 31 |
Ga |
0.00 |
0.79 |
0.00 |
0.79 |
|
| 32 |
Ge |
0.01 |
0.78 |
0.00 |
0.74 |
|
| 33 |
As |
0.02 |
0.72 |
0.00 |
0.71 |
|
| 34 |
Se |
0.01 |
0.77 |
0.01 |
0.66 |
|
| 35 |
Br |
0.03 |
0.78 |
0.00 |
0.58 |
|
| 36 |
Kr |
0.03 |
0.72 |
0.00 |
0.73 |
|
| 37 |
Ru |
0.09 |
0.70 |
0.01 |
0.64 |
|
| 38 |
Sr |
0.07 |
0.78 |
0.01 |
0.72 |
|
| 39 |
Y |
0.01 |
0.79 |
0.01 |
0.70 |
|
| 40 |
Zr |
0.02 |
0.74 |
0.04 |
0.68 |
|
| 41 |
Nb |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.05 |
0.71 |
|
| 42 |
Mo |
0.03 |
0.73 |
0.03 |
0.70 |
|
| 43 |
Tc |
0.07 |
0.69 |
0.04 |
0.72 |
|
| 44 |
Ru
|
0.09 |
0.69 |
0.03 |
0.74 |
|
| 45 |
Rh |
0.05 |
0.68 |
0.03 |
0.73 |
|
| 46 |
Pd |
0.04 |
0.72 |
0.04 |
0.67 |
|
| 47 |
Ag |
0.03 |
0.78 |
0.04 |
0.70 |
|
| 48 |
Cd |
0.05 |
0.78 |
0.03 |
0.74 |
|
| 49 |
In |
0.06 |
0.70 |
0.09 |
0.78 |
|
| 50 |
Sn |
0.07 |
0.75 |
0.06 |
0.73 |
|
| 51 |
Sb |
0.70 |
0.68 |
0.06 |
0.66 |
|
| 52 |
Te |
0.10 |
0.74 |
0.05 |
0.71 |
|
| 53 |
I |
0.09 |
0.68 |
0.03 |
0.75 |
|
| 54 |
Xe |
0.12 |
0.79 |
0.05 |
0.73 |
|
| 55 |
Cs |
0.07 |
0.72 |
0.02 |
0.63 |
|
| 56 |
Ba |
0.15 |
0.77 |
0.06 |
0.69 |
|
| 57 |
La |
0.10 |
0.75 |
0.07 |
0.78 |
|
| 58 |
Ce |
0.11 |
0.74 |
0.07 |
0.70 |
|
| 59 |
Pr |
0.07 |
0.74 |
0.09 |
0.71 |
|
| 60 |
Nd |
0.06 |
0.78 |
0.05 |
0.73 |
|
| 61 |
Pm |
0.09 |
0.70 |
0.05 |
0.73 |
|
| 62 |
Sm |
0.09 |
0.74 |
0.09 |
0.66 |
|
| 63 |
Eu |
0.15 |
0.69 |
0.10 |
0.67 |
|
| 64 |
Gd |
0.16 |
0.69 |
0.10 |
0.74 |
|
| 65 |
Tb |
0.16 |
0.74 |
0.11 |
0.75 |
|
| 66 |
Dy |
0.10 |
0.76 |
0.08 |
0.69 |
|
| 67 |
Ho |
0.16 |
0.75 |
0.08 |
0.75 |
|
68
|
Er |
0.15 |
0.74 |
0.10 |
0.67 |
|
69
|
Tm |
0.11 |
0.70 |
0.09 |
0.72 |
|
70
|
Yb |
0.18 |
0.75 |
0.09 |
0.71 |
|
71
|
Lu |
0.15 |
0.82 |
0.07 |
0.72 |
|
72
|
Hf |
0.12 |
0.84 |
0.09 |
0.69 |
|
73
|
Ta |
0.19 |
0.73 |
0.12 |
0.76 |
|
74
|
W |
0.10 |
0.72 |
0.13 |
0.77 |
|
75
|
Re |
0.14 |
0.77 |
0.12 |
0.77 |
|
76
|
Os |
0.12 |
0.75 |
0.15 |
0.74 |
|
77
|
Ir |
0.24 |
0.75 |
0.10 |
0.71 |
|
78
|
Pt |
0.14 |
0.74 |
0.12 |
0.81 |
|
79
|
Au |
0.22 |
0.80 |
0.10 |
0.73 |
|
80
|
Hg |
0.15 |
0.79 |
0.12 |
0.80 |
|
81
|
Tl |
0.22 |
0.76 |
0.09 |
0.72 |
|
82
|
Pb |
0.23 |
0.75 |
0.14 |
0.66 |
|
83
|
Bi |
0.23 |
0.78 |
0.09 |
0.80 |
|
84
|
Po |
0.21 |
0.80 |
0.21 |
0.76 |
|
85
|
At |
0.14 |
0.72 |
0.12 |
0.73 |
|
86
|
Rn |
0.30 |
0.73 |
0.13 |
0.81 |
|
87
|
Fr |
0.18 |
0.84 |
0.11 |
0.79 |
|
88
|
Ra |
0.25 |
0.80 |
0.15 |
0.73 |
|
89
|
Ac |
0.22 |
0.76 |
0.13 |
0.68 |
|
90
|
Th |
0.23 |
0.78 |
0.11 |
0.80 |
|
| 91 |
Pa |
0.23 |
0.82 |
0.20 |
0.71 |
|
| 92 |
U |
0.25 |
0.84 |
0.14 |
0.74 |
|
| Reference |
|
[1] |
[1] |
[1] |
[1] |
|
Figure 1168 shows backscattering yield of Ga ions for Cu and Si as a function of incidence angle for 100 Ga ions at 30 keV, obtained by TRIM calculations.
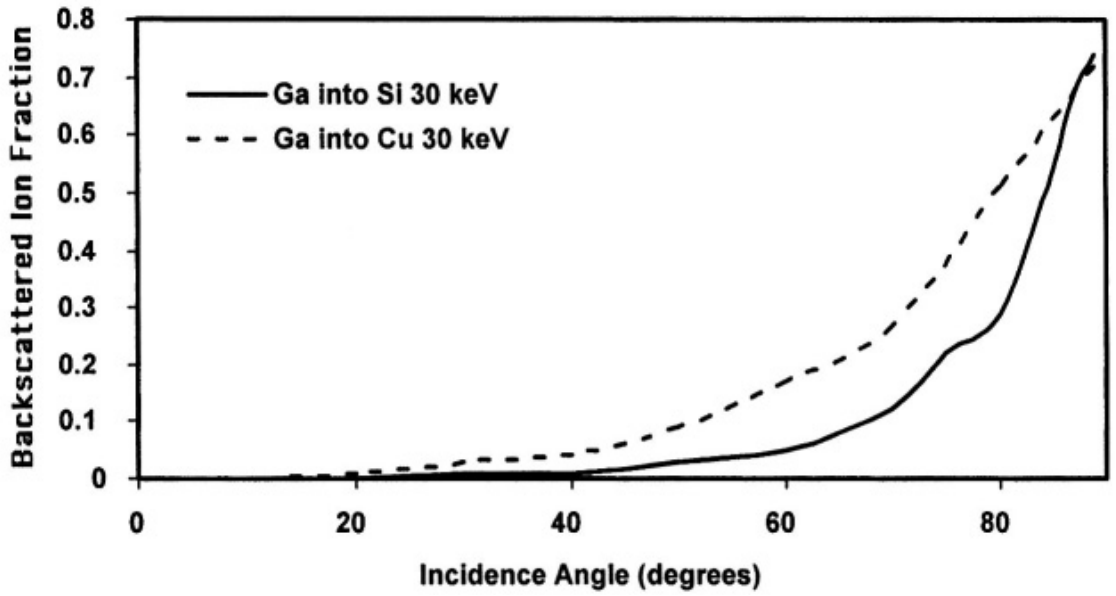
Figure 1168. Backscattering yield of Ga ions for Cu and Si as a function of incidence angle for 100 Ga ions at 30 keV, obtained by TRIM calculations. [1] The incident angle is the angle of incidence with respect to target normal.
|
[1] Lucille A. Giannuzzi and Fred A. Stevie, Introduction to Focused Ion Beams: Instrumentation, Theory, Techniques and Practice, 2005.
|