Table of Contents/Index
Chapter/Index:
Introduction |
A | B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
Appendix
| P (primitive) lattices & their space groups |
|
| Triclinic |
| P1 (1) |
P-1 (2) |
| Monoclinic |
| P2 (3) |
P21 (4) |
| Pm (6) |
Pc (7) |
| P2/m (10) |
P21/m (11) |
| P2/c (13) |
P21/c (14) |
| P21/n |
| Orthorhombic |
| P222 (16) |
P2221 (17) |
| P21212 (18) |
P212121 (19) |
| Pmm2 (25) |
Pmc21 (26) |
| Pcc2 (27) |
Pma2 (Pbm2, 28) |
| Pca21 (Pbc21, P21ab, 29) |
Pnc2 (30) |
| Pmn21 (31) |
Pba2 (32) |
| Pna21 (P21cn, 33) |
Pnn2 (34) |
| Pmmm (47) |
Pnnn (48) |
| Pccm (49) |
Pban (50) |
| Pmma (51) |
Pnna (52) |
| Pmna (53) |
Pcca (54) |
| Pbam (55) |
Pccn (56) |
| Pbcm (57) |
Pnnm (58) |
| Pmmn (59) |
Pbcn (60) |
| Pbca (61) |
Pnma/Pbnm (62) |
| Tetragonal |
| P4 (75) |
P41 (76) |
| P42 (77) |
P43 (78) |
| P-4 (81) |
P4/m (83) |
| P42/m (84) |
P4/n (85) |
| P42/n (86) |
P422 (89) |
| P4212 (90) |
P4122 (91) |
| P41212 (92) |
P4222 (93) |
| P42212 (94) |
P4322 (95) |
| P43212 (96) |
P4mm (99) |
| P4bm (100) |
P42cm (101) |
| P42nm (102) |
P4cc (103) |
| P4nc (104) |
P42mc (105) |
| P42bc (106) |
P-42m (111) |
| P-42c (112) |
P-421m (113) |
| P-421c (114) |
P-4m2 (115) |
| P-4c2 (116) |
P-4b2 (117) |
| P-4n2 (118) |
P4/mmm (123) |
| P4/mcc (124) |
P4/nbm (125) |
| P4/nnc (126) |
P4/mbm (127) |
| P4/mnc (128) |
P4/nmm (129) |
| P4/ncc (130) |
P42/mmc (131) |
| P42/mcm (132) |
P42/nbc (133) |
| P42/nnm (134) |
P42/mbc (135) |
| P42/mnm (136) |
P42/nmc (137) |
| P42/ncm (138) |
| Trigonal |
| P3 (143) |
P31 (144) |
| P32 (145) |
P-3 (147) |
| P312 (149) |
P321 (150) |
| P3112 (151) |
P3121 (152) |
| P3212 (153) |
P3221 (154) |
| P3m1 (156) |
P31m (157) |
| P3c1 (158) |
P31c (159) |
| P-31m (162) |
P-31c (163) |
| P-3m1 (164) |
P-3c1 (165) |
| Hexagonal |
| P6 (168) |
P61 (169) |
| P65 (170) |
P62 (171) |
| P64 (172) |
P63 (173) |
| P-6 (174) |
P6/m (175) |
| P63/m (176) |
P622 (177) |
| P6122 (178) |
P6522 (179) |
| P6222 (180) |
P6422 (181) |
| P6322 (182) |
P6mm (183) |
| P6cc (184) |
P63cm (185) |
| P63mc (186) |
P-6m2 (187) |
| P-6c2 (188) |
P-62m (189) |
| P-62c (190) |
P6/mmm |
| P6/mcc (192) |
P63/mcm (193) |
| P63/mmc (194) |
P6m2 |
| Cubic |
| P23 (195) |
P213 (198) |
| Pm-3 (200) |
Pn-3 (201) |
| Pa-3 (205) |
P432 (207) |
| P4232 (208) |
P4332 (212) |
| P4132 (213) |
P-43m (215) |
| P-43n (218) |
Pm-3m (221) |
| Pn-3n (222) |
Pm-3n (223) |
| Pn-3m (224) |
| Others |
| P105/mmc |
Pm-35 |
| Comparison between Space Group P1 and Space Group Irnmm |
| p-i-n structures |
| Applications of p-i-n structures in EM-related devices |
| p-n junction |
| Built-in potential in p-n junction |
PVC of pn-junction structures/diodes |
| p-well contacts and p-contacts in ICs |
| PVC of p-well contacts in ICs |
PVC of n-contacts in p-well in ICs |
| PVC of p-contacts in n-well in ICs |
| Packaging |
| IC failure induced during wafer packaging and shipping |
| Packing density in some crystal planes |
Packing factor (atomic) in crystals |
| Pair correlation function (PCF) |
Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis |
| Palladium (Pd) |
| EELS measurement of palladium (Pd) |
EDS measurement of palladium (Pd) |
| SEM and STEM observation of Pd (Palladium) particles |
Palladium in ICs |
| Pd-based metallic-glass alloys |
Palladium oxide (PdO) |
| Parabaloid method for image series reconstruction with TEM |
Parallax (film thickness) measurements |
| Parallel illumination in TEM |
Parallel: Comparison of microscope conditions with parallel and convergent beams |
| Paramagnetic materials |
Parallel EELS spectrometer (PEELS) |
| Parasitic aberrations in multipole corrector optics |
Paraxial ray focus |
| Paraxial rays (electrons) in EMs |
Partial coherence of electron source |
| Partial density of states (PDOS) |
Partial cross-sections for inner-shell ionization |
| Partial, total and integral cross-sections for inner-shell ionization |
| Particle & Nanoparticle |
| EDS artifact of measurement on (nano-) particles |
Requirements and preparation of nano-particles TEM samples |
| SEM and STEM observation of Pd (Palladium) particles |
Wave-particle duality |
| Killer particles causing IC failure |
Particle analysis with DM and scripts |
| Requirements and preparation of nano-particles TEM samples |
| Passive voltage contrast (PVC) in FIB and SEM |
| Positive charging case of PVC in FIB and SEM |
Artifacts in PVC in FIB and SEM |
| Advanced mechanisms of PVC contrast |
Negative charging case of PVC in SEM |
| Short failure in IC devices detected by PVC |
PVC of pn-junction structures/diodes |
| PVC of gate contacts |
PVC of n-well contacts in ICs |
| PVC of p-well contacts in ICs |
PVC of n-contacts in p-well in ICs |
| PVC of p-contacts in n-well in ICs |
Equivalent circuit diagram of PVC in FIB and SEM |
| Dependence of PVC generation on area and/or volume of connected conducting materials |
PVC of transistors |
| PVC of capacitors |
Optimized conditions for PVC observations |
| Patches |
| Dark patches |
| Pattern center determination in EBSD |
Patterson method |
| Quartz PCI-AM (Passive Capture Interface - Automated Measurement) |
|
| Patterson space group |
Pauli exclusion principle |
| Automatically indexing TEM electron diffraction patterns using machine learning |
| PC/remote application in EMs |
| Computer- & remote-control on electron microscopes |
Data acquisition and analysis using PC in EMs |
| Peak-detector/peak-stretcher in EDS systems |
Peak pile-up continuum in x-ray/EDS profiles |
| Peak broadenings in EELS |
| Core-loss peak broadening in EELS |
Broadening of EELS zero-loss peak due to phonon scattering |
| Peak-to-background ratios |
| Peak-to-background ratio in EELS |
| Peak splitting in XRD profiles |
Peak identification in EDS measurements |
| Pearson symbols |
Peltier thermoelectric cooling |
| Peltier mechanical cooling |
Pendellösung/Pendellosung fringes in crystals |
| Penetration/diffusion of elements through grain boundaries |
Penetration depth of energetic incident electrons in materials |
| Penetration depth of a laser into materials |
|
| Penning gauge/(cold cathode) ionization gauge |
Pentagonal Penrose tiling |
| Perfect dislocations |
Perfect/ideal lenses in EMs |
| (Peripheral Component Interconnect) PCI based firewire card |
| Peripheral electrons removed by objective aperture |
Peripheral electrons emitted from electron guns |
| Periodic/step features in HRTEM images |
| HCP Structure at Grain Boundaries in FCC Materials |
9R structure at grain boundaries in FCC materials |
| Periodic Table |
| Periodic table for analytical
TEM (EDS/EELS) analysis |
Periodic table for EELS analysis |
| Periodic table for EDS analysis |
Atomic Weight of Elements in Periodic Table |
| Most Common Crystal Structure of Elements in Periodic Table |
Alkali metals, Halogens, Transition metals, and Noble Gases in Periodic table |
| Metals, Metalloids, and Nonmetals in periodic table |
Periodic table of X-ray absorption edges |
| Periodic table for electron affinity |
Periodic table for atomic & ionic radii and valence states of elements |
| Abundance in Earth's Crust of the elements |
Periodic table for SIMS measurement |
| Digital Micrograph script to create a periodic table |
| Permittivity of materials |
| Perovskite structures |
| Double perovskite crystalline structures |
HRTEM imaging of perovskite structures |
| Goldschmidt tolerance factor |
CaTiO3 |
| Extra electron diffraction spots from perovskite crystalline structures |
[100] zone axis of perovskite structures |
| Perovskite-like ferroelectrics |
| LaMnO3 |
Bipolar resistive switching in perovskite insulators |
| Phase in EMs |
| Phase of Fourier components in HRTEM images |
Phase shift of electrons induced by objective lens |
| Phase-contrast in TEM images |
Phase correlation function (PCF) |
| Phase shift from defocus and spherical aberration |
Geometrical Phase Analysis (GPA) |
| Minimum (phase-)contrast in (HR)TEM imaging with Gaussian defocus |
Maximum (phase-)contrast in (HR)TEM imaging (with Scherzer defocus) |
| Phase object approximation (POA) |
Phase contrast transfer function/phase distortion function |
| Phase extension procedure |
Phase-contrast microscopy |
| Phase shift of incident electrons induced by TEM specimen |
Phase shift of electrons depending on scattering angle in TEM/STEM |
| Scherzer phase plate |
Beam convergence angle/coherence effects on phase shift |
Phase-plate electron microscope/TEM with phase-plate
|
| Zernike-type phase plate for TEMs |
Hilbert-type phase plates for TEMs |
| Phase of materials |
| Phase identification with XRD and its procedure |
Crystalline phase analysis by EELS and its plasmon |
| Phase separation in metallic glasses |
Indexing of crystal structures |
| Phase-induced splitting of reflections in electron diffraction patterns |
| Phase transition of materials |
| First-order phase transitions |
First-order ferroelectric phase transitions |
| Second-order phase transitions |
Shuffle transformation |
| Phase change optical storage media |
Rewritable phase-change optical memory disks |
| Diffusionless phase transformation |
Driving force for the phase transition in materials |
| Martensitic transformation |
Phase transitions inducing ferroelectricity |
| Phonon excitation by electrons in EMs |
| Vibration of atoms/phonon |
| Phonon excitation and thermal diffuse scattering (TDS) of electrons in EMs |
Phonons formed in EMs versus heating |
| Phonon effect on electron diffraction patterns |
Phonon effect on TEM imaging |
| Responding time of phonon emission for electron irradiation |
Broadening of EELS zero-loss peak due to phonon scattering |
| Phonon-electron scattering |
| Broadening of diffraction peak & phonon-electron scattering |
Debye phonon model |
| Phosphorus (P) |
| EDS measurements of phosphorus (P) |
EELS measurements of phosphorus (P) |
| AlGaInP |
Compound semiconductor |
| Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) |
Ni5P2 |
| Phosphine (PH3) |
P-based metallic-glass alloys |
| Phosphor used in electron spectrum detectors/cameras |
CCD sensors/detectors with phosphor and fiber-optic coupling |
| Photodiode array (PDA) for EELS |
Photo-diode array (PDA) detectors |
| Photoelectrons |
Photographic plate/photo-film for image recording in EMs |
| Photomultiplier (PM) |
| Scintillator-photomultiplier (PM) system |
| Photons |
| Responding time of photon emission for electron irradiation |
Energy/wavelength of X-ray "particles" (photons) |
| Photonic technology |
| Photovoltaic |
| Photovoltaic devices |
Techniques of physical failure analysis (PFA) for ICs
|
Physical gate length |
| Physical and chemical constants, and unit conversion |
Picoammeter |
| Pi (π) bonds |
| Piezo |
| Piezo-controlled energy-selecting slit in EELS device & GIF camera |
Piezoelectric materials |
| Piezoresponse atomic-force microscopy (PFM) |
Piezo drive TEM/STEM holders |
| Pinhole lens for objective lens in SEMs |
Pirani gauge |
| Pipes used in EMs |
Poisson distribution (statistics) |
| Pivot point/rocking point/tilt & shift and their purities in TEM |
Pixel in digital imaging cameras |
| CMOS Monolithic Active Pixel Sensors (MAPS) direct electron detectors |
Hybrid Pixel Array Detector (PAD): A direct electron detector |
| Pixel resolution for recording CBED patterns |
Pixel size in EM imaging |
| Planes in lattice systems of crystals |
| A-, M-, R-, and C-planes of sapphire crystal |
Cleavage plane of crystals |
| Close packed planes and directions in crystals |
Determination of Miller indices of planes |
| Plane wave of electron beam |
| Plane wave and interference pattern in electron holography |
Excitation coefficient for plane wave incidence |
| Diffraction of plane wave from multiple point sources |
| EM sample preparation of SiC (Silicon Carbide) materials |
| Plasma |
| Plasma cleaning and plasma cleaners used for EM sample cleaning |
Plasma cleaning of FIB prepared specimens |
| Cleaning of hydrocarbon contamination by oxygen radicals in EMs |
| Plasmon (plasma oscillation/plasma resonance) |
| Applications of plasmon mode in EELS for nanostructures |
Plasmon peaks from thick TEM samples |
| Table of surface & bulk plasmon energy in EELS |
Plasmon measurement in EELS |
| Surface & bulk plasmon energy in EELS |
Crystalline phase analysis by EELS plasmon |
| Plasmon mean free path |
Surface plasmons formed in thin specimen in EMs |
| Maximum intensity of plasmon energy loss peak |
Interband plasmon peak energy |
| Plasmon signal affected by core-loss transitions in EELS |
Number of valence electrons involved in plasmon scattering |
| Analysis of surface plasmon resonances affected by energy resolution |
Cross section of plasmon scattering |
| Sample thickness determination using EELS/FETEM |
Origin of change of plasmon energy |
| Plastic deformation |
Plastic deformation of metallic glasses
|
Free volume change in amorphous materials induced by deformation |
| Platinum |
| EDS measurement of platinum (Pt) |
EELS measurement of Platinum (Pt) |
| Platinum Deposition by FIB |
Amorphization of STO induced by e-beam Pt deposition |
| FePt alloys |
Platinum in ICs |
| PtSi in ICs |
Pt-based metallic-glass alloys |
| Plural/multiple scattering of electrons |
Pneumatic apertures |
| Pnicogen |
| Intermetallic compounds between 3d transition metal and pnicogen |
| Point ROI on Gatan DigitalMicrograph |
| Point |
| Number of lattice points (atoms) per unit cell |
Point resolution in EMs |
| Point-spread and its function |
Lattice point/motif/basis |
| Point defects |
| Detection of point defects |
Saturation of point defects |
| Voids generated during TEM sample preparation |
Point defects created in FIB-EM sample preparation |
| Frenkel pair |
|
| Atomic point defects |
Electronic point defects |
| Point defects (vacancy & interstitial) generated in Ar-milling |
| Point groups/symmetries (32) (Space group) |
| Holohedral point groups |
Merohedral point groups |
| Crystallographic point group notations/description |
Determination of point group |
| Determination of point groups of cubic systems |
Point groups of crystals of biological macromolecules |
| Polar point groups for ferroelectricity |
Relationship between diffraction group and point group |
| Crystal structure |
Point group |
| Triclinic |
1 |
| -1 |
| Monoclinic |
2 |
| m |
2/m |
| Orthorhombic |
222 |
| mm2 |
mmm |
| Tetragonal |
4 |
| -4 |
4/m |
| 422 |
4mm |
| -42m |
4/mmm |
| Trigonal |
3 |
| -3 |
32 |
| 3m |
-3m |
| Hexagonal |
6 |
| -6 |
6/m |
| 622 |
6mm |
| Trigonal prismatic: -62m (or D3h) |
6/mmm |
| Cubic |
23 |
| m-3 |
432 |
| -43m |
m-3m |
| Others |
-53m (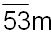 ) ) |
| Polar net |
Polar point groups for ferroelectricity |
| Pole (plane normal) in electron stereographic projection |
| Angle between two planes/plane normals/poles measured by Wulff net |
| Polepiece |
| Nonuniform magnetic properties of pole-piece material |
Objective polepiece in EMs |
| Polepiece in magnetic prism of energy filters |
Upper-/lower-objective polepiece in TEMs |
| Pole piece gaps in EM systems |
Effect of configuration of objective polepieces on STEM/TEM spatial resolution |
| Polycrystalline materials |
| Electron diffraction patterns of polycrystalline materials |
Polysilicon and diffused resistors |
| Polycrystalline silicon in ICs |
Polycrystalline silicon in solar cells |
| Polymer |
| Analytical investigations of polymer |
TEM specimen grids for EDS analysis |
| Polymer TEM sample preparation |
In situ FIB lift-out TEM sample preparation |
| Polytype layer compounds |
| Portable/desktop/tabletop SEM |
Popup windows and input dialogs of scripts for DM |
| Positive (cathode) & negative (anode) electrode materials for lithium batteries |
Position effects of TEM sample |
| Position of parts in TEM system |
| Sample location in TEM system |
Location of EELS spectrometers in TEM system |
| Position of EDS detector in EMs |
Position and length of aberration correctors |
|
| Post-column energy filters & spectrometers |
Post-fields of objective lens |
| Potassium (K) |
| EDS measurement of potassium (K) |
EELS of potassium (K) |
| K2O·7Nb2O5 crystals |
Seignette salt/Rochelle salt (NaKC4H4O6•4H2O) |
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) etching
|
| Potential |
| Periodic potential of crystals |
Effect of periodic potential of crystal on STEM imaging |
| Fourier coefficients of electrostatic potential |
| Power |
| High power devices (of ICs) |
Low standby power devices |
| Power spectra of bright-field (BF) TEM micrographs |
Power-law fit: a background fitting model |
| Power supply |
| Electron-gun high-voltage power supply in EMs |
Power supplies for quadrupole/octupole aberration correctors |
| Precession electron diffraction (PED) |
| Comparison between conventional electron diffraction and PED, and PED applications |
Diffraction intensity in precession electron diffraction |
| Kinematical effects of PED (precession electron diffraction) |
Dynamical effects of PED (precession electron diffraction) |
| Precession electron diffraction applications on nanostructures |
| Precision of measurements |
Precipitation of transition metals |
| Precursor gases used in ion-beam/FIB/electron-beam induced depositions |
| Preferential phenomena |
| Preferential electron-beam etching of grain boundaries |
Preferential destruction of multilayers in FIB milling |
| Pre-field in EMs |
| Objective pre-field lens |
| Pressurized air for EM parts |
Prewitt edge filter (operator) |
| Prices of EM and related system and services |
| Primary electrons (PE) in EMs |
| Energy dissipation of primary electrons (PE) in materials |
Maximum ranges of primary electron beam in EMs |
| Dependence of dopant contrast in Si on accelerating voltage of PE |
| Primitive great circle in electron stereographic projection |
Primitive (P) lattices |
| Primitive unit cell determination by electron diffraction |
| Prisms |
| Möllenstedt–Düker biprisms in optical and electron microscopes |
EELS detector/spectrometers |
| Probability |
| Probability of containing m atoms in a single atom column in crystal |
Cross section (probabilities) of electron scattering (Introduction: Elastic & Inelastic) |
| Probes in mechanical, electron and ion systems |
|
| Mechanical, electron and ion probe diameters |
| Probe in EMs |
| Probe-forming/objective aperture for STEM imaging |
Lenses for fine probe/beam formation in EMs |
| Probe-forming aperture in EMs |
Electron-probe intensity distribution depending on aberrations |
| Electron-Beam-Probing (eBP) |
Comparison between Electron-Beam-Probing (eBP) and Laser Voltage Imaging/Probing (LVI/LVP) |
| Electron Voltage Imaging (EVI) and Electron Voltage Probing (EVP) |
Clock edge detection via electron beam probing |
| Wave function of focused probe in STEM/SEM |
|
| Dependence of electron probe/beam current on probe size in EMs |
Beam/probe size in EMs |
| Probe current in EMs |
Probe current density |
| Probe current measurement with Faraday cage in EMs |
Measurement of electron probe current with EELS spectrometer |
| Probe current affected by aberration corrections |
Measurement of probe current |
| Evaluation of probe size in EMs |
Probe diameter in EMs |
| Procedures |
| Phase identification procedure by CBED |
CBED Operation Procedure |
| Probe-forming Cs-corrector |
| Processing |
| EM image processing and deconvolution |
TEM image formation process |
| Processes and mechanisms of secondary electron generation |
Profile analysis in integrated circuits (IC) |
| Profile function on Gatan DigitalMicrograph |
Program and software examples for EM-related simulations |
| Projected potential model for TEM specimens |
Projection-diffraction symmetry |
| Publication number related to electron microscopes per year |
| Projector lenses in TEMs/STEMs |
| Projector lenses & camera lengths in TEMs |
Projector crossover |
| Projector lenses and image/diffraction distortion in EMs |
Projector Lens Alignment (PLA) |
| Back focal plane of projector lens in TEM |
Properties |
| Semiconductor properties |
Nonuniform magnetic properties of pole-piece material |
| Propane torch for EMs |
| Proteins |
| Electron crystallography of proteins |
| Proximity effect in lithography |
| Pseudo-binary systems |
| Pseudo-binary system Nb2O5/WO3 |
| Pseudo-weak phase-object approximation |
|
| Pulsed electron beam in electron microscopy |
|
| Generating a pulsed electron beam using microwave and pulsed RF-based guns in EMs |
|
| Laser-based pulsed electron beam generation for EMs |
Beam blanking deflector in EMs and FIB |
| Generating a pulsed electron beam using field emission with modulated voltage in EMs |
Generating a pulsed electron beam using an RF-cavity chopped-beam in EMs |
| Pulsed thermally induced voltage alteration (TIVA) |
|
| Pumping system in EMs |
| Comparison between common pumps used in EMs |
Vacuum range/efficiency & pump combination |
| Roughing pumps |
Oil-diffusion Pump |
| Silicon oils from diffusion pump |
Sputter ion pump (SIP) |
| Classification of vacuum pumps |
| Pumps: Exhaust pumps |
| Rotary vacuum pumps |
Diffusion pumps |
| Turbo-molecular pump (TMP) |
| Pumps: Compressive/mechanical pumps |
| Rotary vacuum pumps |
Scroll vacuum pumps |
| Turbo-molecular pump (TMP) |
| Pumps for high and ultra-high vacuums |
| Turbomolecular pump |
Cryopump/cold traps for vacuum & cryogenic (adsorption) pumps |
| Pumps: Trapping pumps/Entrainment pumps |
| Ion getter pumps |
Cryopump/cold traps for vacuum & cryogenic (adsorption) pumps |
| Purchase/buy/sale/service of EM systems |
Purchase/buy/sale/service of TEM systems and acceptance specifications of new systems |
| Python |
Pyroelectric materials |

