=================================================================================
Turbomolecular pumps (often called turbo-pumps) is a type of compressive pumps. They have many parts moving at high speeds (20,000 - 90,000 rpm, depending on the size of the pump and the desired base pressure) with a turbine (similar to a jet turbine) to pull gas molecules from the microscope and then force them out of the back of the pump. A multi-stage, turbine-like rotor rotates in the housing (see Figure 4322a). In such systems, bladed disks are designed to enhance the flow of gas. A rotor together with a stator disk forms a compression stage and a pump normally has ten to forty stages. These stages collectively force the gas molecules from the chamber to pump them out.

Figure 4322a. An example of turbomolecular pumps.
Because turbo pumps are kinetic pumps, they can reach very high vacuum by using momentum transfer. When a molecule strikes the high speed blades, the moving blades impart a portion of their momentum to the molecules and change their direction to flow into the next stage of the pump. This process continues until the molecules reach the mechanical pump.
Although turbo pumps are extremely robust and reliable, they do have a few drawbacks of causing the pump to completely fail. Due to the high-speed mechanical movement, the failure rate of turbo-pumps is higher than diffusion pumps. Operating at pressures higher than 10-2 torr can cause blade banding, warping, or even breaking or crashing. However, some new pumps are able to automatically slow down or shut off if the pressure is too high. On the other hand, to avoid vibrations, a magnetic buoyant-type rotor should be used.
Again, turbomolecular pumps in high vacuum systems, such as TEMs and SEMs, cannot work directly against atmospheric pressure and need a mechanical pre-vacuum pump in order to function as shown in Figure 4322b. The turbomolecular pumps can reach an ultimate vacuum of 5x10-10 torr. Turbomolecular pumps have pumping capacity of 50 - 500 l/s. Turbo-pumps have been used to pre-pump the specimen chamber in TEMs but are normally backed with dry mechanical pumps in modern microscopes. The high vacuum produced by diffusion pumps, turbomolecular pumps and ion getter pumps is normally measured by Penning gauges.
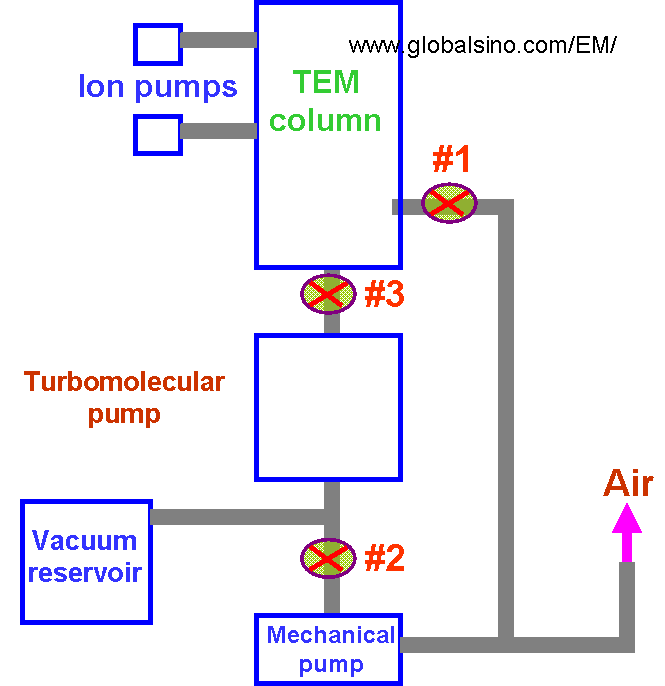
Figure 4322b. Schematic illustration of pumping system in TEMs.
Turbo-pumps do not use oil so that they do not introduce hydrocarbons to contaminate the microscope.
As shown in Figure 4322c (a), in most modern TEMs, the electron gun, top lenses, and specimen chamber are maintained at ultra-high vacuum by an ion pump, while the viewing screens and photographic chamber are maintained at a lower vacuum, which is referred to as high vacuum, by either a diffusion pump or a turbomolecular pump. This vacuum level is backed by a mechanical (rotary) pump. Actually, in a typical TEM system, rotary or scroll pump are used to evacuate the compressed air molecules from the exhaust port of the turbo-molecular pump. However, some TEMs have lower vacuum in the specimen chamber as shown in Figure 4322c (b).
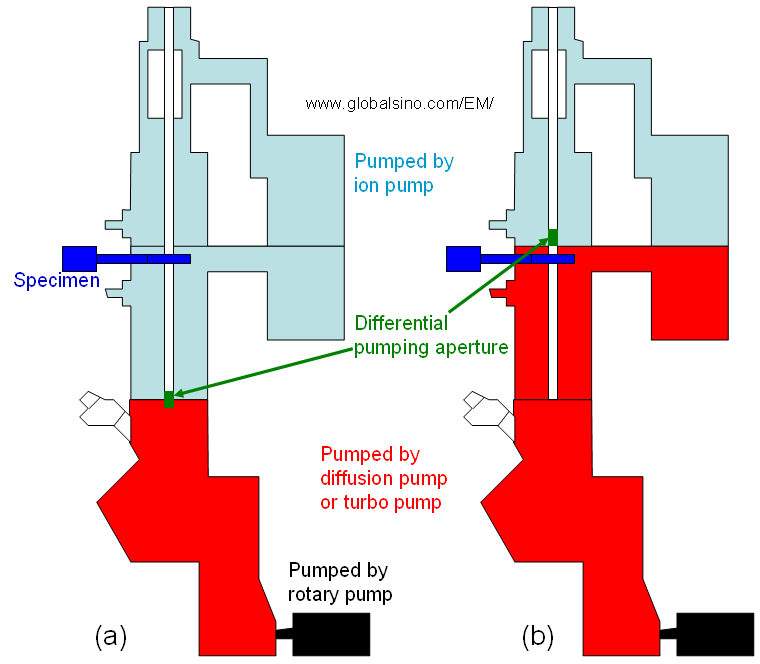
Figure 4322c. Vacuum in TEMs: (a) Modern TEMs, and (b) Some TEMs.
Mostly, microelectronics industry has the need of the cleanest microscope columns. For instance, after the semiconductor wafers, containing numerous microelectronic devices, are observed with SEMs, various fabrication processes will continue. Therefore, the wafers cannot be contaminated during SEM observation. The vacuum configuration of the microscopes for this application would probably have a scroll pump used to rough out and to back a turbomolecular pump for the specimen chamber. In addition, ion getter pumps are typically attached to the electron electron gun and the upper portion of the column. In this case, the three types of pumps can provide the cleanest SEM system.
|

