Chapter/Index: Introduction | A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
Appendix
Interaction of X-Ray with Materials
| In the interaction of X-rays with materials, some of the x-rays will be absorbed, and some will be transmitted or diffracted through the material listed in Table 1205. The degrees of absorption/fluorescence, Compton and Rayleigh scatter and transmission depends on:
i) X-Ray energy
ii) Sample thickness
iii) Materials density
vi) Materials composition.
Table 1205. Interaction of X-ray with materials.
Interaction |
Mechanism |
Application |
| Rayleigh scatter, Diffracted
X-rays |
Scattering without loss of energy (re-radiate waves with the same frequency), from bound charges, coherent scatter |
X-ray diffraction (XRD) |
| Compton scatter |
Scattering with loss of energy, from loosely bound charges, incoherent scatter |
|
| Fluorescence |
When absorption occurs |
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) |
| Transmitted
X-rays |
Direct transmission |
|
| Auger electron |
Electron ejected from atoms by absorbing energy from X-ray |
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) |
| Photoelectrons |
Emitted electrons |
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) |
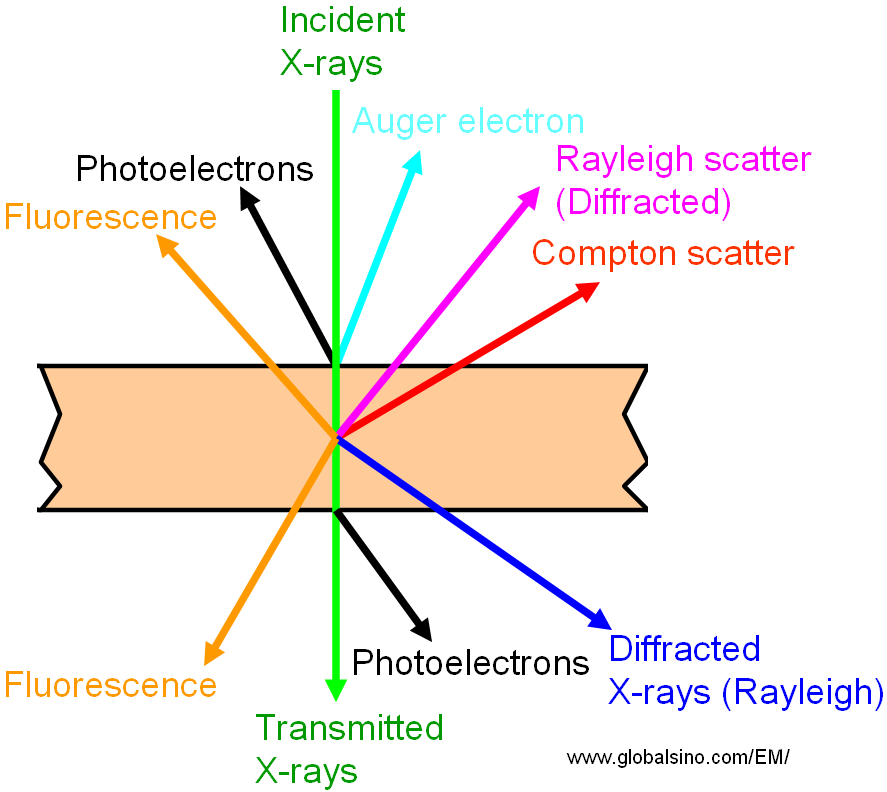
Figure 1205. Phenomena of X-ray interaction with materials.
|
