Chapter/Index: Introduction | A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
Appendix
Ion Extractor in FIB
| Figure 2487 shows the schematic illustration of dual beam FIB/SEM. The angle (α) between the electron beam and ion beam is normally in the range of 52 and 54°. The description and operation principle of all the components in the system can be found in the online book.
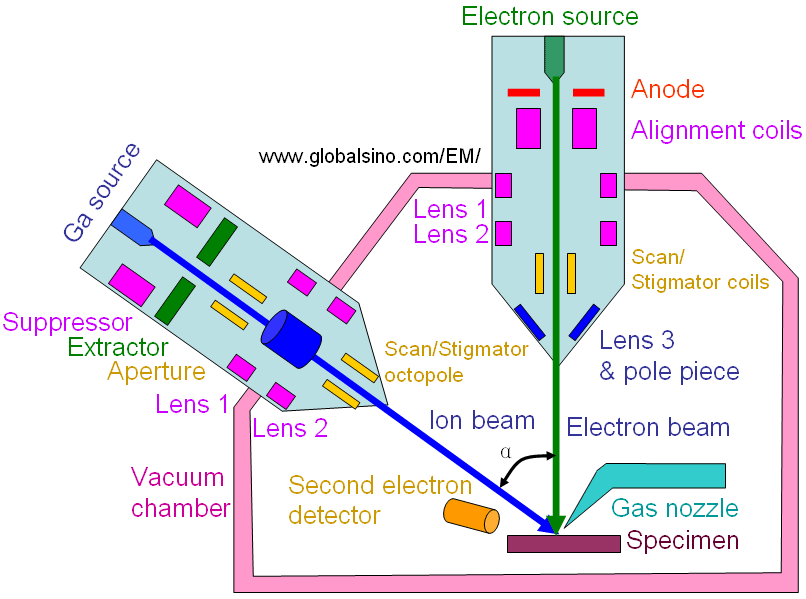
Figure 2487. Schematic illustration of dual beam FIB/SEM.
Table 2487. The function of each part in the FIB.
Part |
Function |
LMIS |
Ion source |
Suppressor |
Improves the distribution of extracted
ions |
Extractor |
High tension used for ion extraction: Typical accelerating voltage in FIB systems ranges from 1 to 30 keV |
Spray aperture |
First refinement |
1st lens (condenser lens) |
Parallelize the ion beam: probe forming |
Upper octopole |
Stigmator |
Beam defining aperture
|
Defines current: A set of apertures define the probe size and provides a range of ion currents (10 pA – 30 nA) |
Blanking deflector |
Beam blanking: Beam blankers are used to deflect the beam away from the centre of the column |
Blanking aperture |
Beam blanking |
Lower octopole |
Raster scanning |
2nd lens (objective lens) |
Beam focusing |
|
