=================================================================================
Figure 2483a shows the dependence of ionic sputtering yields on the energies of different ions in the energetic beams. Here, the incident ions (Au, Nd, In, Ga, Co, Si, N, and Li) are normal to the silicon (Si) target surface. In FIB, the ions in the energetic beam are normally Ga+ ions.
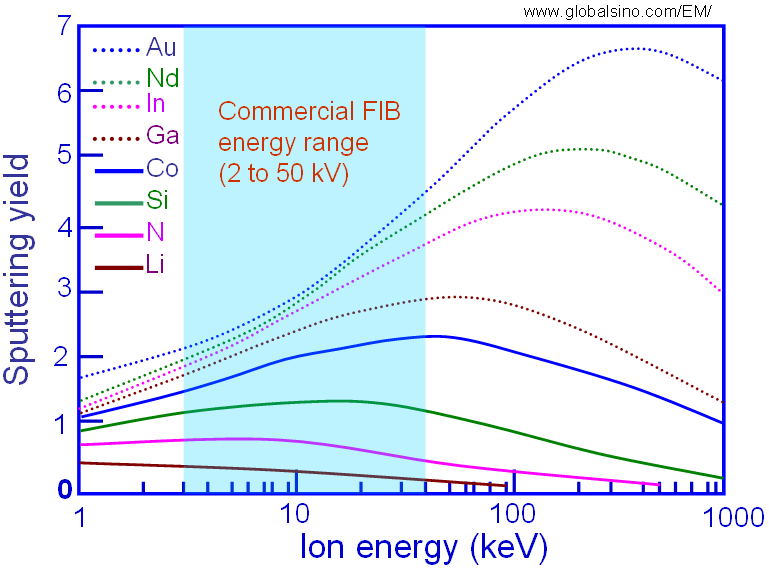
Figure 2483a. The dependence of ionic sputtering yields on ion energies. The target material is silicon.
Figure 2483b shows the dependence of ionic sputtering yields on the energies of different ions in the energetic beams. Here, the incident ions (Au, Nd, In, Ga, Co, Si, N, and Li) are normal to the silicon (Si) target surface. In FIB, the ions in the energetic beam are normally Ga+ ions.

Figure 2483b. The dependence of ionic sputtering yields on ion energies. The target material is silicon.
| Table 2483. Examples of Ga ion sputtering yields on different material surfaces. The incident angle is the angle of incidence with respect to target normal. This angle is schematically shown in page2455. |
| Material or atomic number |
|
Ga ion sputtering yields (atoms/ion or molecules/ion) |
Note |
| Voltage |
5 kV |
5 kV |
30 kV |
30 kV |
30 kV |
|
| Angle |
0 degree |
88 degrees |
0 degree |
52 degrees |
88 degrees |
|
| GaAs |
|
|
5.6 |
|
|
|
| Glass |
|
|
0.68 |
|
|
|
| SiO2 |
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
|
| Water (H2O) ice |
|
|
7 - 12
(83 - 123 K) |
|
18 |
Cryo-FIB |
| 1 |
H |
0.22 |
36.09 |
0.79 |
|
90.78 |
|
| 2 |
He |
0.65
|
29.00 |
1.20 |
|
58.14 |
|
| 3 |
Li |
0.94 |
19.55 |
1.73 |
|
50.23 |
|
| 4 |
Be |
1.34
|
15.37 |
2.22 |
|
35.77 |
|
| 5 |
B |
0.92 |
11.39 |
1.45 |
|
29.36 |
|
| 6 |
C |
0.81 |
9.38 |
1.69 |
|
22.93 |
|
| 7 |
N |
1.53 |
15.35
|
2.61 |
|
45.43 |
|
| 8 |
O |
2.42 |
17.72 |
4.75 |
|
37.00 |
|
| 9 |
F |
2.05 |
13.87 |
3.62 |
|
39.19 |
|
| 10 |
Ne |
3.22 |
18.18 |
5.14 |
|
47.28 |
|
| 11 |
Na |
3.14 |
16.31 |
4.93 |
|
42.25 |
|
| 12 |
Mg |
3.28 |
15.61 |
4.91 |
|
42.54 |
|
| 13 |
Al |
2.67
|
13.29 |
3.47-4.2 |
|
34.78 |
|
| 14 |
Si |
1.73 |
7.98 |
2.1-2.78 |
|
27.61 |
|
| 15 |
P |
1.44 |
9.71 |
2.91 |
|
29.10 |
|
| 16 |
S |
2.37 |
10.36 |
3.48 |
|
27.66 |
|
| 17 |
Cl |
3.03 |
13.69 |
4.06 |
|
37.49 |
|
| 18 |
Ar |
1.75 |
7.41 |
2.69 |
|
18.22 |
|
| 19 |
K |
1.40 |
10.37 |
2.11 |
|
17.39 |
|
| 20 |
Ca |
1.68 |
7.47 |
2.35 |
|
14.59 |
|
| 21 |
Sc |
1.52 |
5.82 |
1.60 |
|
11.62 |
|
| 22 |
Ti |
1.41 |
5.70 |
2.28 |
|
13.28 |
|
| 23 |
V |
1.32 |
5.92 |
2.90 |
|
13.96 |
|
| 24 |
Cr |
2.94 |
8.37 |
2.3-5.15 |
|
20.61 |
|
| 25 |
Mn |
4.98 |
11.66 |
8.17 |
|
33.55 |
|
| 26 |
Fe |
3.74 |
7.81 |
5.58 |
|
24.49 |
|
| 27 |
Co |
5.37 |
8.53 |
7.39 |
|
24.63 |
|
| 28 |
Ni |
5.26 |
9.20 |
9.69 |
|
27.13 |
|
| 29 |
Cu |
8.13 |
12.04 |
8.37 |
|
32.71 |
|
| 30 |
Zn |
15.29 |
22.66 |
22.80 |
|
51.20 |
|
| 31 |
Ga |
5.62 |
8.33 |
5.93 |
|
20.57 |
|
| 32 |
Ge |
2.93 |
5.82 |
4.54 |
|
15.58 |
|
| 33 |
As |
10.50 |
15.97 |
13.64 |
|
34.74 |
|
| 34 |
Se |
4.57 |
8.57 |
7.72 |
|
22.57 |
|
| 35 |
Br |
5.10 |
6.96 |
4.50 |
|
19.50 |
|
| 36 |
Kr |
4.53 |
8.58 |
4.42 |
|
18.56 |
|
| 37 |
Ru |
3.73 |
8.39 |
5.37 |
|
18.52 |
|
| 38 |
Sr |
3.90 |
7.12 |
3.74 |
|
16.08 |
|
| 39 |
Y |
1.94 |
4.11 |
4.17 |
|
9.85 |
|
| 40 |
Zr |
2.20 |
3.97 |
3.87 |
|
9.72 |
|
| 41 |
Nb |
3.05 |
4.25 |
4.18 |
|
10.31 |
|
| 42 |
Mo |
3.86 |
4.86 |
6.05 |
|
13.63 |
|
| 43 |
Tc |
16.63 |
16.13 |
22.27 |
|
48.35 |
|
| 44 |
Ru
|
5.96 |
5.85 |
9.91 |
|
13.75 |
|
| 45 |
Rh |
6.92 |
7.24 |
9.61 |
|
18.90 |
|
| 46 |
Pd |
9.94 |
9.39 |
14.23 |
|
27.19 |
|
| 47 |
Ag |
8.51 |
7.66 |
13.43 |
|
26.31 |
|
| 48 |
Cd |
17.42 |
15.57 |
18.47 |
|
51.00 |
|
| 49 |
In |
7.31 |
8.31 |
13.12 |
|
19.30 |
|
| 50 |
Sn |
6.05 |
6.82 |
8.17 |
|
15.88 |
|
| 51 |
Sb |
5.57 |
7.79 |
7.88 |
|
21.05 |
|
| 52 |
Te |
7.91 |
7.61 |
8.37 |
|
20.41 |
|
| 53 |
I |
4.13 |
7.43 |
5.08 |
|
16.92 |
|
| 54 |
Xe |
5.53 |
7.40 |
7.66 |
|
18.99 |
|
| 55 |
Cs |
6.57 |
9.29 |
8.33 |
|
19.53 |
|
| 56 |
Ba |
5.04 |
6.92 |
7.73 |
|
13.89 |
|
| 57 |
La |
3.24 |
4.25 |
4.30 |
|
10.93 |
|
| 58 |
Ce |
3.36 |
4.05 |
5.14 |
|
15.40 |
|
| 59 |
Pr |
4.51 |
4.30 |
7.28 |
|
15.15 |
|
| 60 |
Nd |
3.64 |
4.58 |
3.57 |
|
14.31 |
|
| 61 |
Pm |
5.49 |
8.52 |
9.88 |
|
21.37 |
|
| 62 |
Sm |
7.21 |
8.91 |
8.40 |
|
24.35 |
|
| 63 |
Eu |
4.94 |
8.29 |
9.51 |
|
17.27 |
|
| 64 |
Gd |
3.44 |
5.41 |
4.27 |
|
10.79 |
|
| 65 |
Tb |
3.67 |
5.44 |
5.34 |
|
13.73 |
|
| 66 |
Dy |
5.23 |
6.37 |
6.87 |
|
15.93 |
|
| 67 |
Ho |
6.18 |
6.47 |
7.19 |
|
14.04 |
|
68
|
Er |
5.82 |
6.71 |
8.70 |
|
16.35 |
|
69
|
Tm |
7.01 |
8.18 |
11.12
|
|
20.15 |
|
70
|
Yb |
7.99 |
8.63 |
13.23 |
|
20.76 |
|
71
|
Lu |
4.19 |
4.79 |
4.33 |
|
9.21 |
|
72
|
Hf |
4.39 |
4.29 |
6.55 |
|
14.47 |
|
73
|
Ta |
4.49 |
3.87 |
7.26 |
|
11.45 |
|
74
|
W |
4.37 |
4.37 |
7.59 |
8 |
11.21 |
|
75
|
Re |
5.66 |
4.47 |
8.74 |
|
11.09 |
|
76
|
Os |
6.31 |
5.18 |
8.30 |
|
13.17 |
|
77
|
Ir |
8.22 |
6.18 |
10.69 |
|
15.96 |
|
78
|
Pt |
7.14 |
6.00 |
9.76
|
|
15.88 |
|
79
|
Au |
10.19 |
8.08 |
15.75-17 |
|
24.13 |
|
80
|
Hg |
26.83 |
21.04 |
48.16 |
|
59.84 |
|
81
|
Tl |
8.76 |
10.72 |
15.23 |
|
26.64 |
|
82
|
Pb |
9.97 |
8.69 |
15.05 |
|
25.95 |
|
83
|
Bi |
7.98 |
6.34 |
11.92 |
|
17.84 |
|
84
|
Po |
6.66 |
6.60 |
12.13 |
|
20.89 |
|
85
|
At |
6.78 |
7.86 |
11.00 |
|
22.66 |
|
86
|
Rn |
7.02 |
7.15 |
15.18 |
|
16.19 |
|
87
|
Fr |
5.66
|
5.86 |
7.92
|
|
19.67 |
|
88
|
Ra |
3.43 |
4.36 |
4.20 |
|
10.18 |
|
89
|
Ac |
6.26 |
7.46 |
12.48 |
|
18.82 |
|
90
|
Th |
3.24 |
3.52 |
5.94 |
|
8.87 |
|
| 91 |
Pa |
9.94 |
7.89 |
20.13 |
|
21.01 |
|
| 92 |
U |
6.56 |
4.56 |
8.28 |
|
12.22 |
|
| Reference |
|
[1] |
[1] |
[1 - 6] |
[6] |
[1] |
|
[1] Lucille A. Giannuzzi and Fred A. Stevie, Introduction to Focused Ion Beams: Instrumentation, Theory, Techniques and Practice, 2005.
[2] Jing Fu, Process Modeling and Simulation of Focused Ion Beam Milling of Water Ice in a Cryogenic Environment, PhD thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, 2008.
[3] P. J. Heard, J. R. A. Cleaver, and H. Ahmed, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 3 (1985).
[4] H. Yamaguchi, A. Shimase, S. Haraichi, and T. Miyauchi, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 3, 71 (1985).
[5] J. Melngailis, C. R. Musi, E. H. Stevens, M. Utlaut, E. M. Kellogg, R. T. Post, M. W. Geis, and R. W. Mountain, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 4, 176 (1986).
[6] Other sources.
|